Figure 4.
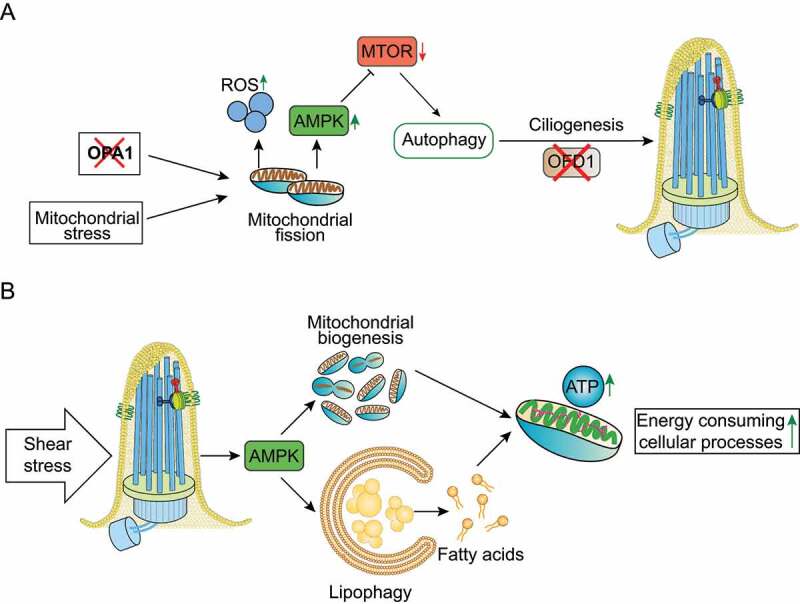
Mitochondria-autophagy-cilia crosstalk models. (a) Mitochondrial stress, such as depletion of the pro-fusion OPA1 gene, and ROS generation stimulate autophagy by activating AMPK and inhibiting the MTOR pathway. Mitochondrial stress-induced autophagy acts as a cytoprotective process by promoting ciliogenesis through enhanced degradation of OFD1. (b) Shear stress induced by biological fluids stimulates AMPK-dependent selective degradation of lipid droplets by autophagy (lipophagy), contributing to the production of fatty acids that provide mitochondrial substrates to generate ATP and produce energy. Moreover, AMPK stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis, which contributes to ATP production. The concomitant mitochondrial biogenesis and lipophagy contribute to control ATP-dependent cellular mechanisms.
