Figure 1.
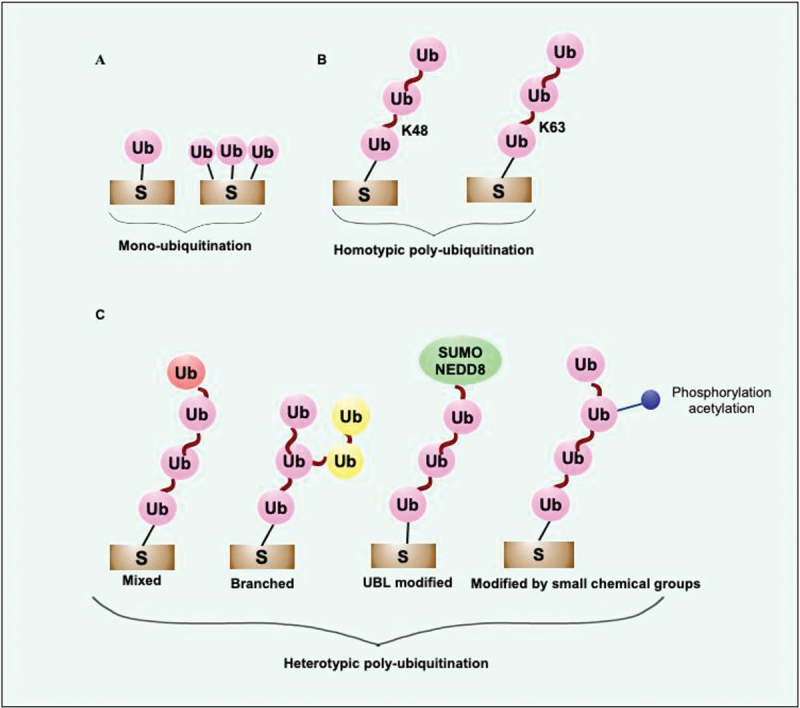
Diverse Ub-signals communicate different biological messages. (a) The diverse Ub-linkages coordinate different biological outcomes such as mono or multi-mono ubiquitination transmit signals for localization, control the activity of ubiquitinated substrates, proteolysis mediated by Ub-proteasome system, and autophagy. (b) K48 and K11 linkages usually transmit signals for degradation of short-lived folded proteins performed by 26S proteasome. K48-linked chains transmit signals for autophagic removal of invading pathogens and misfolded protein aggregates. K63-linked Ub chains transmit signals to remove aggregated proteins and participate in xenophagic clearance of invading cytosolic bacteria by autophagy. Diverse non-degradative processes are regulated by K63 linkages, including activation of DNA damage repair, assembly, and activation of signaling complexes. The main functions of K48- and K63-linked Ub chains are known. However, the crucial roles of newly discovered atypical linkages, including K6, K27, K29, and K33, are less known. Met1-linked linear chain takes part in removing invading pathogens, damaged mitochondria and activates the NFKB1 signaling pathway. (c) Small molecule modifiers of Ub such as acetylation, phosphorylation, and neddylation control various Ub functions. The functions of more complex hetero conjugated Ub are emerging now. S, substrate; Ub, ubiquitin; NEDD8, NEDD8 ubiquitin like modifier.
