Figure 4.
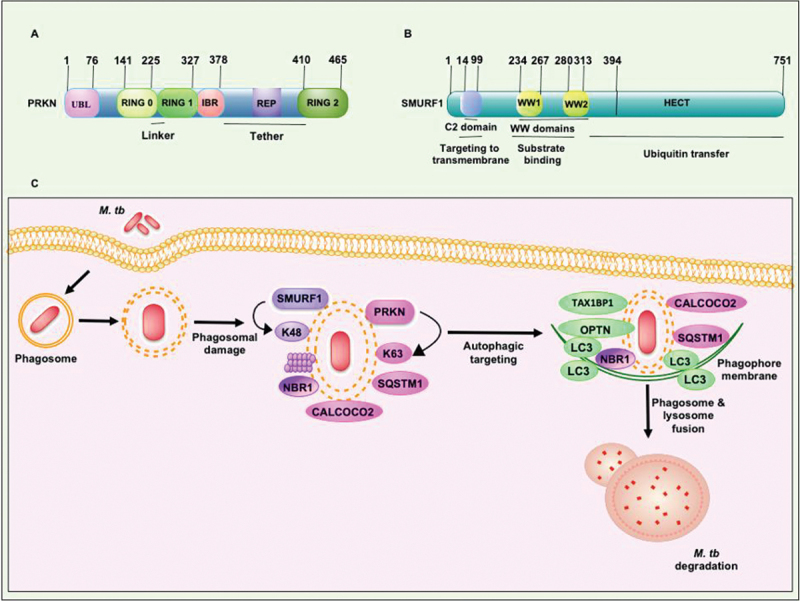
Structural features of PRKN and SMURF1 E3-Ub ligases which execute xenophagy mediated clearance of M. tb. (a) RING1 domain of PRKN consists binding site for Ub-conjugating E2 enzyme. RING2 domain of PRKN contains catalytic cysteine to form a covalent linkage with Ub. The other conserved domains, such as the UBL domain and REP linker region, sandwiched between the RING2 and IBR domains, inhibit RING1 binding to E2. The RING0 domain partially covers the catalytic cysteine residue present in the RING2 domain. (b) The N-terminal C2 domain binds phospholipids and plays an essential role in SMURF1 localization to the membrane. WW domains of SMURF1 are protein interaction domains required for binding with the targets. The transfer of Ub to the protein substrate is governed by the catalytically active C-terminal domain of the HECT family of E3-Ub ligases. The molecular size of both the E3-Ub ligases is shown. (C) PRKN and SMURF1 E3-Ub ligases provide immunity against M. tb. PRKN and SMURF1 ubiquitinate M. tb and its associated membranous structure in the cytosol to recruit autophagy receptors SQSTM1, CALCOCO2, and NBR1. The engagement of LC3 to the phagophore membrane and consequent fusion to the lysosome targets M. tb to xenophagy. REP, repressor element of PRKN.
