Figure 1: Associations between prenatal OH-PAH metabolites and asthma outcomes at 4–6 years.
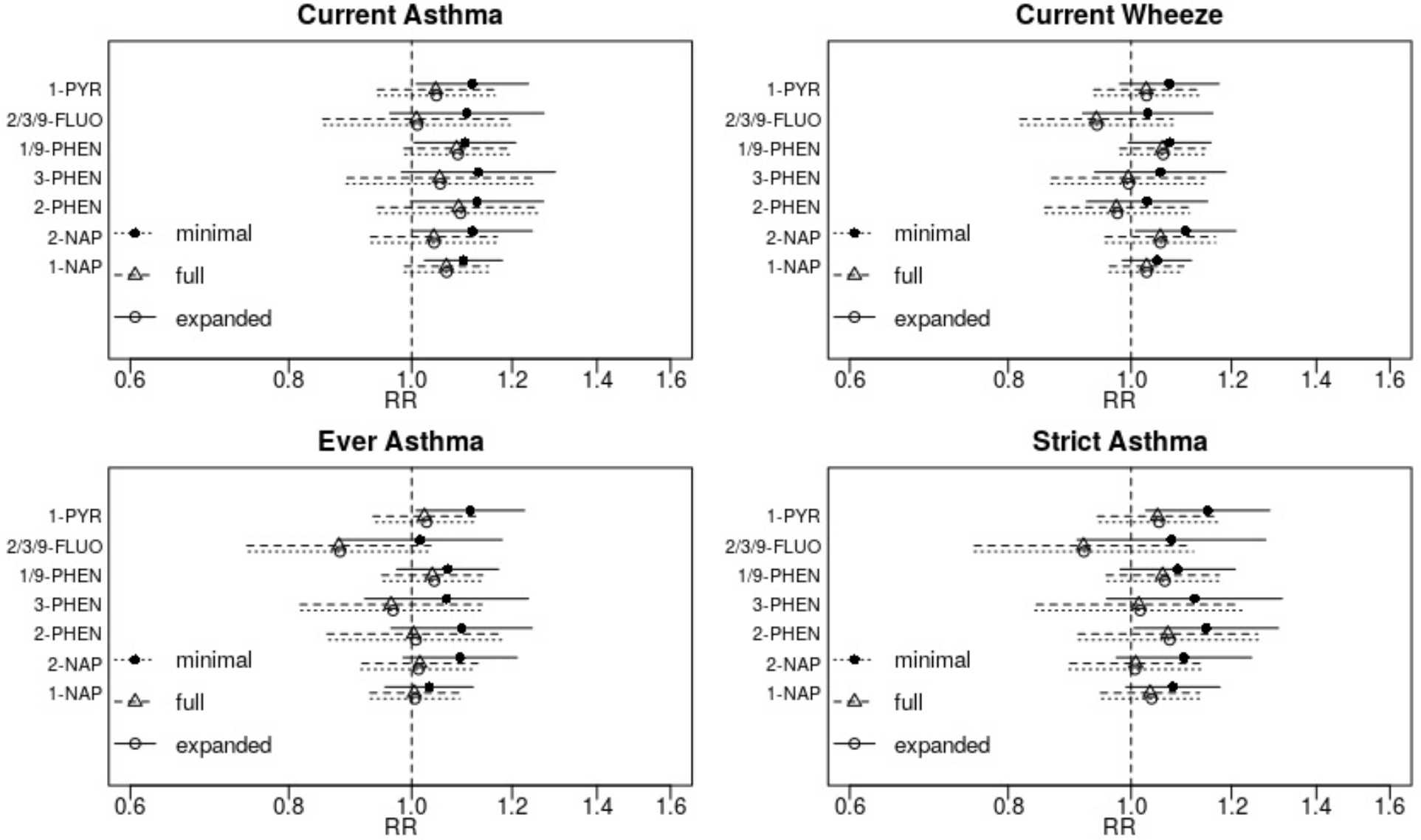
Adjusted relative risks (RR) and 95% confidence intervals were scaled to a two-fold increase in individual OH-PAH metabolite. Associations were estimated using Poisson regression with robust standard errors and adjusted as follows: (minimal model) child age at assessment, child sex, study site, batch of OH-PAH analysis, and urinary specific gravity; (full model) all covariates in minimal model plus maternal age, education, race, pre-pregnancy BMI, household income, parity, maternal history of asthma, enrollment year, postnatal smoke exposure, and season of birth; (expanded) all covariates in full model plus gestational age at birth and birthweight.
Abbreviations: OH-PAH – mono-hydroxylated-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon; 1-PYR - 1-hydroxypyrene; 2/3/9 -FLUO – combined 2- and 3- and 9-hydroxyfluorene; 1/9-PHEN – combined 1- and 9-hydroxyphenanthrene; 3-PHEN - 3-hydroxyphenanthrene; 2-PHEN - 2-hydroxyphenanthrene; 2-NAP - 2-hydroxynaphthalene; 1-NAP - 1-hydroxynaphthalene.
