Figure 1B:
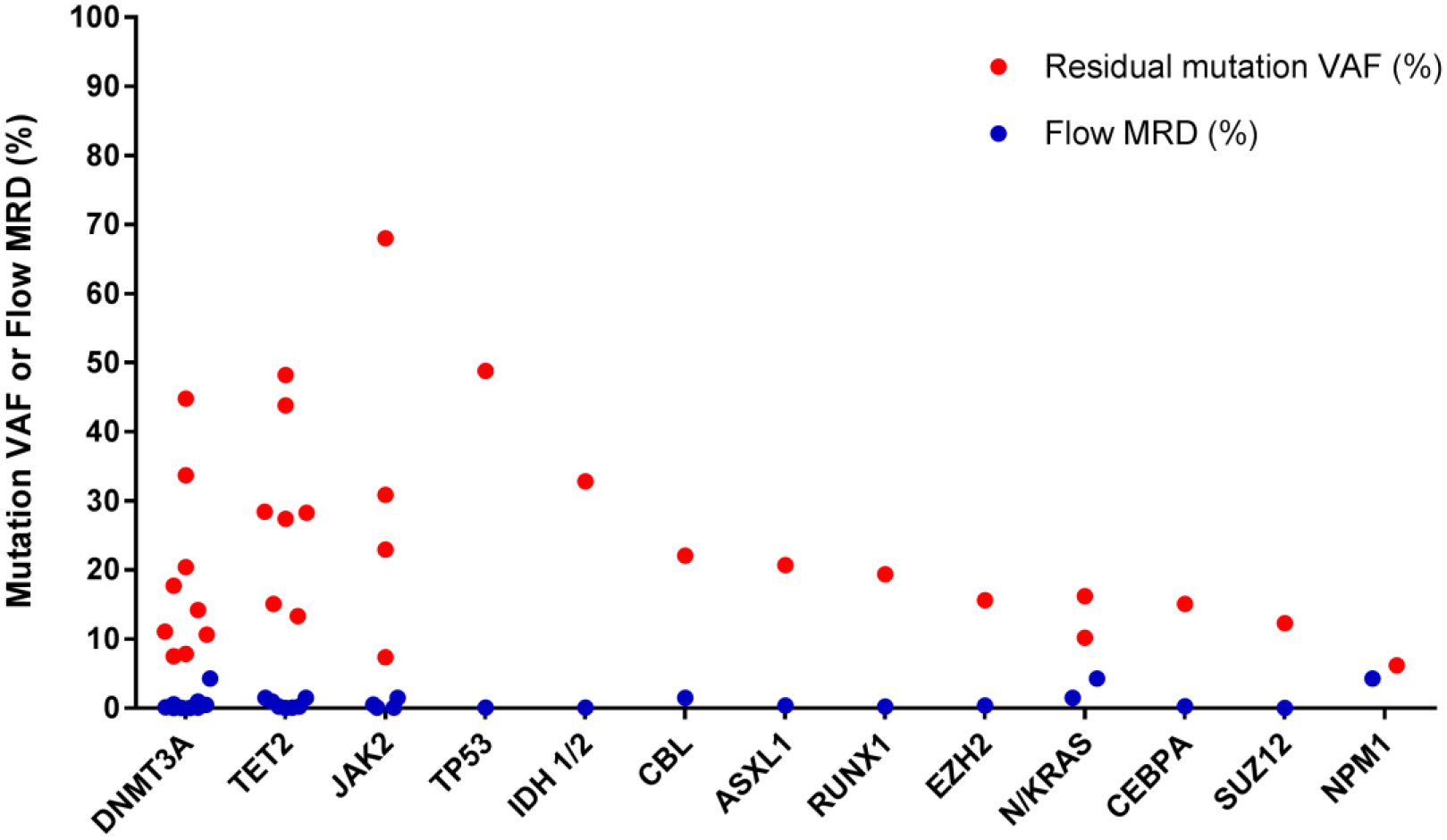
Comparison of residual mutation and flow MRD burden pre HCT
Residual disease in the blast compartment quantified by MFC was matched to the VAF of residual mutations quantified by NGS on the same bone marrow sample for patients who were in hematologic CR/CRi at the time of transplant but who had residual mutations called and had MFC residual disease assessment performed (n=17). The VAF (%) of residual mutations (residual mutations defined by VAF ≥5%) and the percentage of aberrant blasts are plotted on the same Y-axis grouped by leukemia gene. In the vast majority of cases MFC was quantified to be <1% while residual leukemia alleles were quantified ≥5% suggesting that these mutations are present in cells outside of the leukemic blast compartment.
