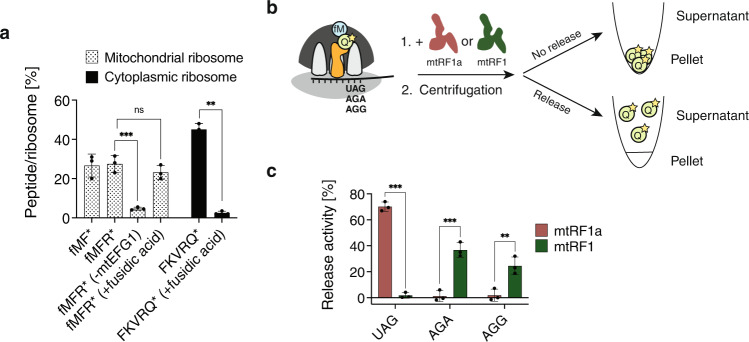
Fig. 5. mtRF1 specifically acts on non-canonical stop codons AGA/AGG.
a In vitro translation assay using mitochondrial or cytosolic ribosomes. Up to five amino-acylated tRNAs were added to the translation mixture. Elongation was assessed by measuring incorporation of radioactively labeled amino acids (*). Specificity of mitoribosomal translation was tested by the absence of mtEFG1 or by addition of fusidic acid. Means and SD of n = 3 independent experiments. Unpaired two-tailed t-test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns = not significant). Only relevant statistics are highlighted. b Schematic representation of the in vitro mitochondrial translation termination assay. Post-translocation complexes (POST2) containing fMQ-tRNAQ* in the P-site and either canonical stop codon UAG or non-canonical stop codons AGA/AGG in the A-site were prepared. MtRF1a/mtRF1-dependent release of dipeptide was assayed by co-sedimentation. Radioactive glutamine was used for detection. c In vitro release activity of mtRF1a and mtRF1 at UAG/AGA/AGG codons. Means and SD of n = 3 independent experiments. Unpaired two-tailed t-test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).