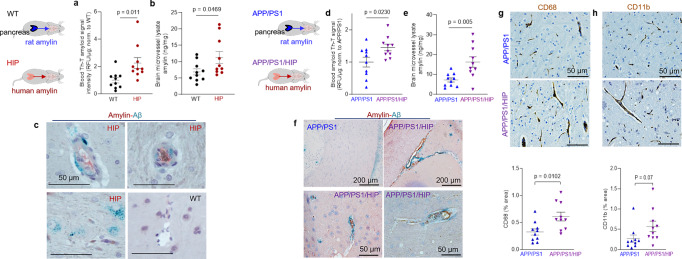
Fig. 3. Cerebrovascular amylin-Aβ deposition induced by amyloid-forming human amylin secreted from the pancreas.
a Thioflavin T (Th T) fluorescence signal intensities in blood lysates from HIP rats and WT littermates (age 15-16-months; n = 10 males/group). b Amylin concentrations in brain microvessel lysates in HIP and WT rats similar to those in (a) (n = 10 males/group). c IHC analysis of HIP rat brains showing Aβ deposits (green) in perivascular spaces and amylin accumulation (brown) within the lumen. (n = 5 males/group; age 15–16-months). d Average Thioflavin T (Th T) fluorescence signal intensities in blood lysates from APP/PS1/HIP and APP/PS1 littermates age 15–16-months (n = 10 rat males/group). e Amylin concentrations in brain microvessel lysates from same rats as above. f Representative IHC micrographs of brain sections from APP/PS1/HIP and APP/PS1 rats co-stained with anti-amylin (brown) and anti-Aβ (green) antibodies (n = 5 males/group; age 15–16-months) (3 slides/brain). Representative IHC images and analysis of phagocytic microglia (CD68) (g) and vascular monocyte recruitment (CD11b) (h) in brain sections from APP/PS1/HIP vs APP/PS1 rat males (n = 10 males/group; age 16-months). Data are means ± SEM; unpaired t-test for all panels.