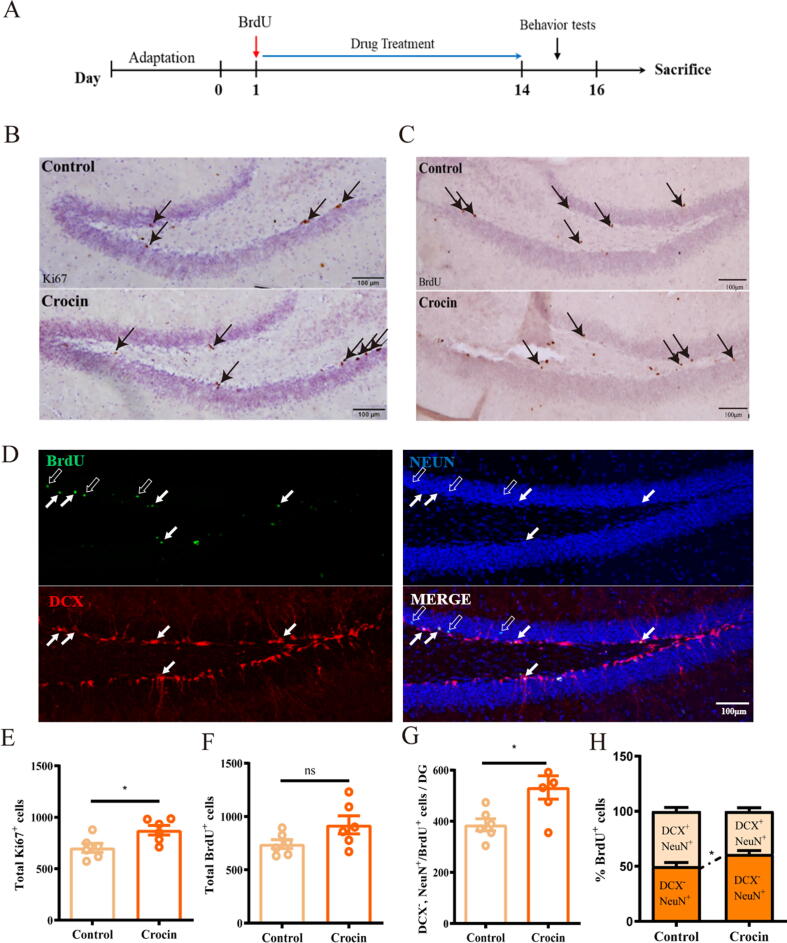
Fig. 2.
Crocin improved adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus. (A) Time line of BrdU injection and drug treatment. (B) Dividing cells (arrows) were identified using Ki67 immunohistochemistry in crocin-treated or control group. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) BrdU immunohistochemistry (gray-brown) was used for detecting 2-week survival cells (arrows), Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) Representative images of DG area showed four types of cells: BrdU+ cells (green) which co-express strong DCX (red) or NeuN (blue); BrdU unlabeled DCX+/NeuN+ immature neurons (denoted by solid arrows); BrdU unlabeled DCX- /NeuN+ mature neurons (denoted by hollow arrow). (E-G) Quantification of Ki67+, total BrdU+ and NeuN+/DCX-/NeuN+ cells. (H) The percentage of DCX- /NeuN+ mature neurons in crocin-treated group or control group. Results are presented as mean ± SEM. Unpaired student’s t-test. *p < 0.05; ns, no significance.