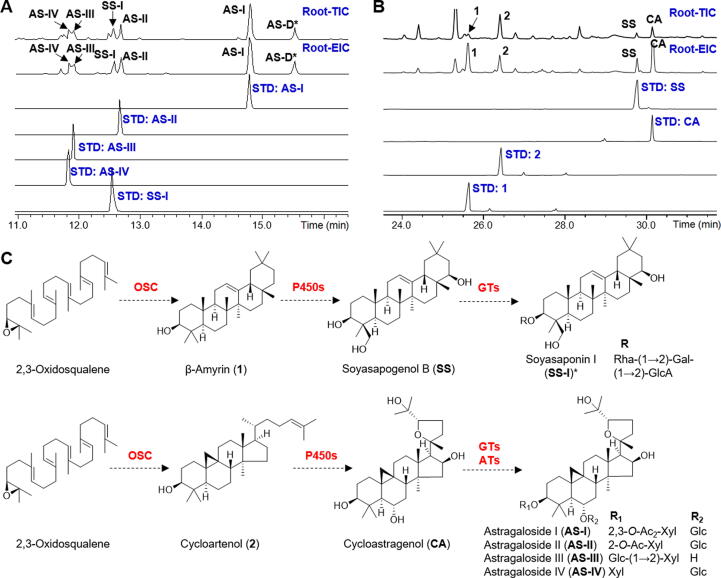
Fig. 1.
Chemical analysis of A. membranaceus and the proposed biosynthetic pathways for its major saponins. (A) LC/MS analysis of a 3-year-old root. TIC, total ion chromatogram; EIC, extracted ion chromatogram. In EIC, m/z 913.48 ([AS-I + HCOO]-), m/z 871.47 ([AS-II + HCOO]-), m/z 829.46 ([AS-III + HCOO]-/[AS-IV + HCOO]-), m/z 941.51 ([SS-I-H]-), and m/z 953.47 ([AS-D-H]-) were extracted. (B) GC/MS analysis of a 3-month-old root. In EIC, m/z 218.2 (1), 339.3 (2), 306.3 (SS), and 215.2 (CA) were extracted. All compounds were identified by comparing with reference standards except for AS-D (identified by HR-MS/MS, Fig. S2A). (C) Proposed biosynthetic pathways of oleanane-type and cycloartane-type saponins in A. membranaceus. P450, cytochrome P450. GT, glycosyltransferase. AT, acyltransferase. Rha, rhamnose. Gal, galactose. GlcA, glucuronic acid. Glc, glucose. Xyl, xylose. Ac, acetyl.