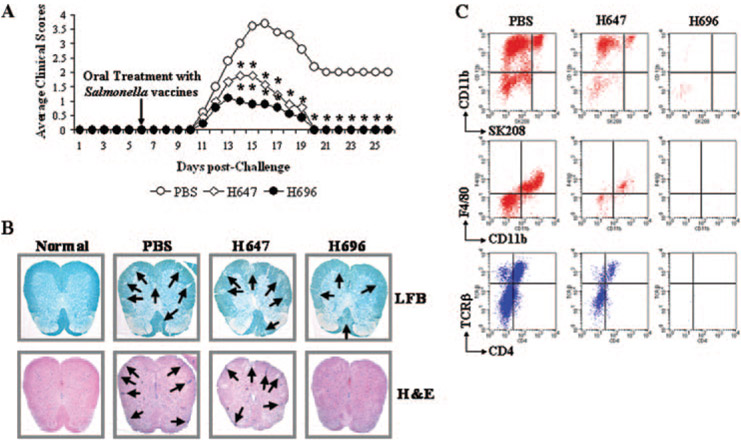
FIGURE 1.
Oral Salmonella-CFA/I (H696) treatment reduced EAE clinical scores in PLP139–151-challenged SJL/J mice (A) and decreased spinal cord demyelination (B) and inflammation (B and C). A, Mice therapeutically treated with H696 showed a significant reduction in their clinical scores with all mice recovering from EAE. Mice treated with Salmonella vector (strain H647) also recovered, but presented greater clinical scores when compared with PBS-treated mice. Depicted are the combined results from four separate experiments for a total of 20 mice/group: *, p < 0.001 for PBS vs H647 and PBS vs H696. B, H696-treated group showed minimal demyelination (LFB) and inflammatory (H&E stain) cell infiltration (indicated by arrows) at 14 days postchallenge when compared with PBS-dosed group; the H647-treated mice showed increased demyelination and inflammation. Representative samples from six mice are depicted. C, FACS analysis of spinal cord leukocytes was performed 14 days after challenge to assess the types of inflammatory cells: neutrophils, CD11b+SK208+; macrophages, CD11b+SK208−F4/80+; and T cells, TCRβ+. Minimal leukocytes were detected in H696-treated mice unlike that observed for PBS- or H647-treated mice; representative samples of five mice per group are depicted.