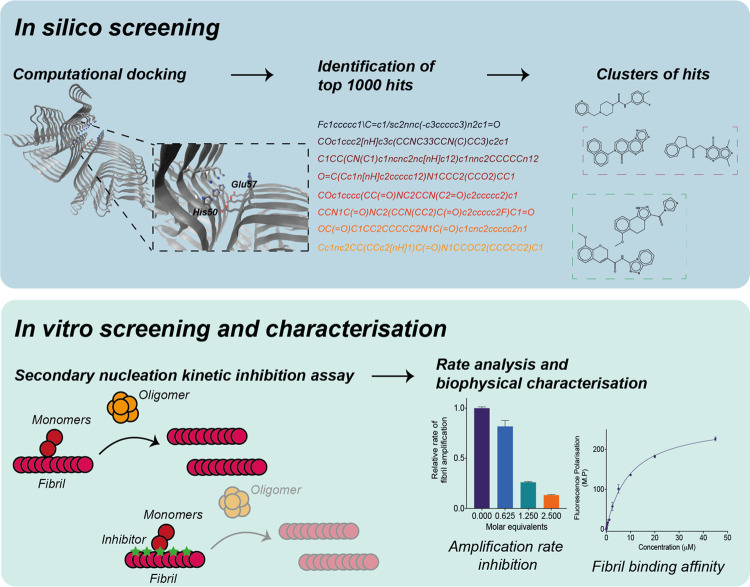
Figure 1.
Combined structure-based and kinetic-based approach to identify small molecules that bind α-synuclein fibrils and inhibit its aggregation. In the first step, computational docking is performed on a large library of small molecules. The top candidates are then clustered to identify a subset of chemically diverse compounds that exhibit high predicted binding scores for α-synuclein fibrils. Subsequently, these compounds are experimentally validated through a kinetic assay for their ability to inhibit the secondary nucleation aggregation of α-synuclein by binding to the surface of fibrils. Further rate constant analysis and fibril-binding experiments allow for the positive compounds to be characterized based on both their inhibition of the kinetic assay, as well as their binding affinity toward α-synuclein fibrils.