Fig. 1.
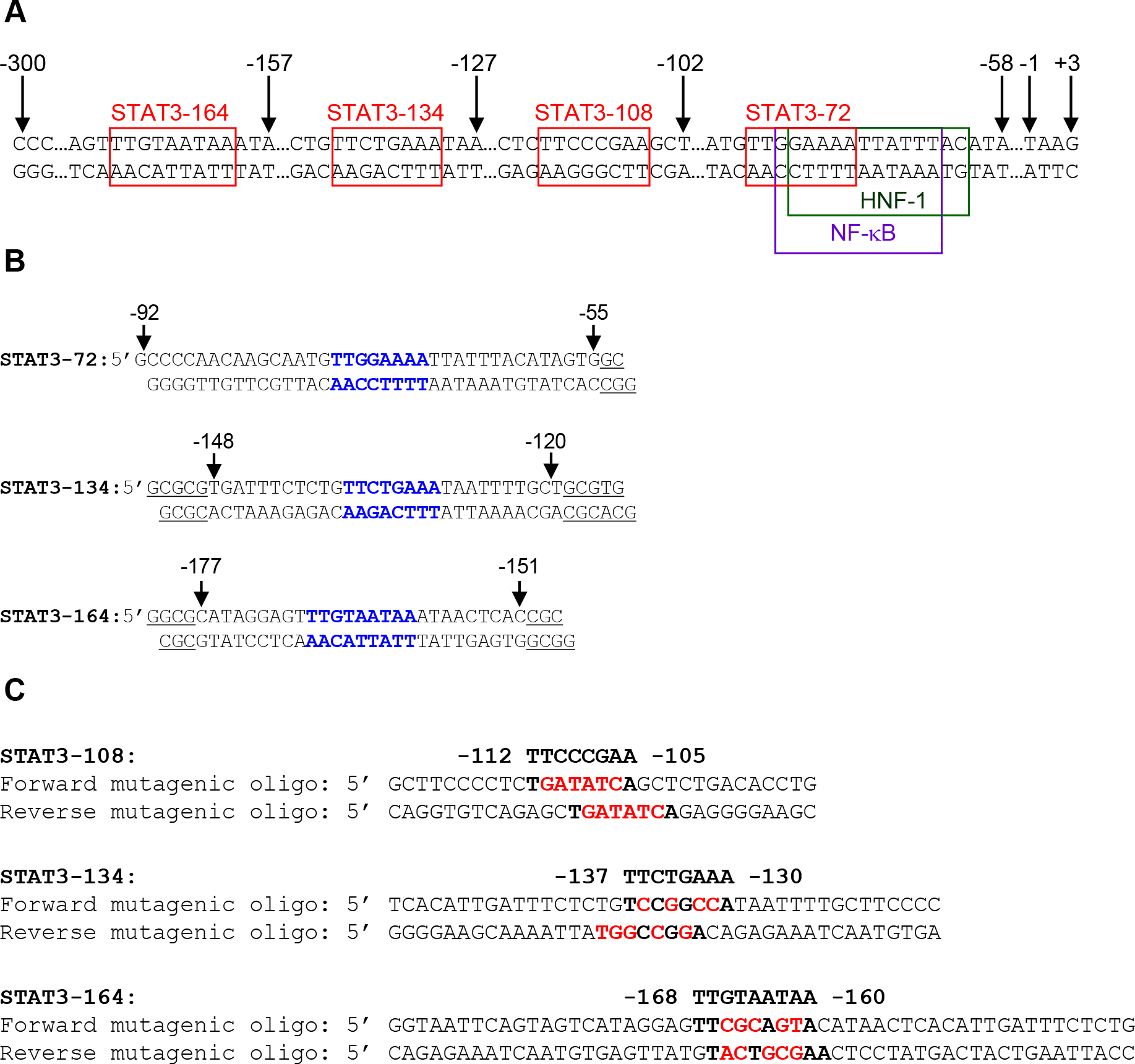
(A) Partial nucleotide sequence of the −300 to +3 region of the CRP gene. The four STAT3-binding sites centered at positions −72 (−69 to −76), −108 (−105 to −112), −134 (−130 to −137) and −164 (−160 to −168) on the promoter are shown in red boxes. The STAT3 site at position −72 overlaps the binding sites for transcription factors HNF-1 and NF-κB. (B) Sequences of the double-stranded oligos derived from the CRP promoter (numbered on the top) and used as probes in EMSA. The STAT3 sites are shown in bold. The underlined nucleotides are not from the CRP promoter; these nucleotides were added to the ends of the oligos according to the instructions from the manufacturer of the radioactive end-labelling kit. (C) Pairs of forward and reverse mutagenic oligo primers used for site-directed mutagenesis of the CRP promoter. The STAT3 sites centered at positions −108, −134 and −164 are shown in bold letters; the mutated bases are shown in red. The primers were designed according to the instructions from the manufacturer of the mutagenesis kit.
