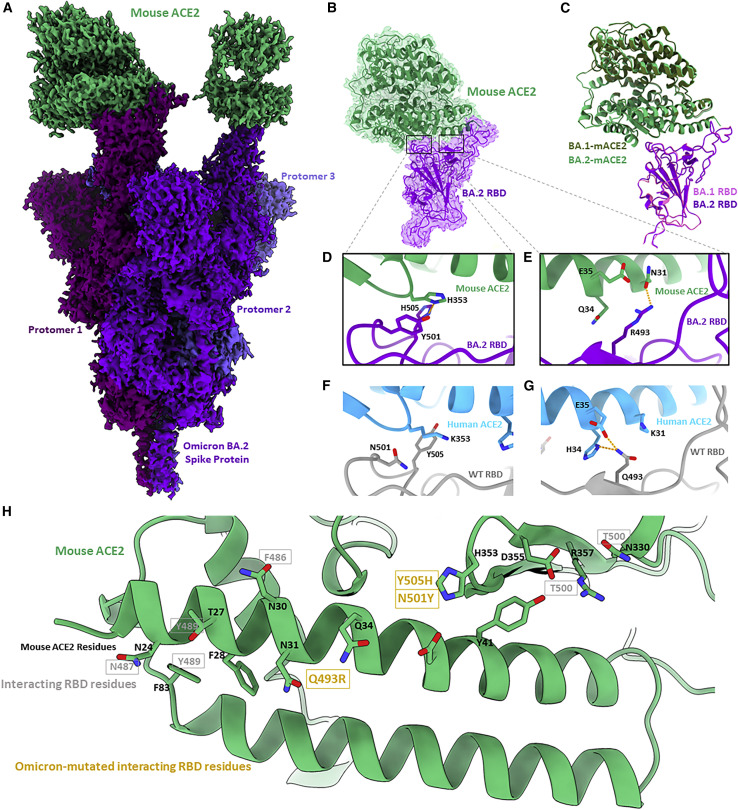
Figure 3.
Cryo-EM structure of the Omicron BA.2 S protein-mouse ACE2 complex
(A) Cryo-EM density map of BA.2 S protein in complex with mouse ACE2 at 2.5 Å. Mouse ACE2 is shown in green, and protomers of the BA.2 S protein are shown in shades of purple.
(B) Focus-refined cryo-EM density map and fitted atomic model of the BA.2 RBD-mouse ACE2 (mACE2) complex at 2.7 Å.
(C) Aligned atomic models of the BA.1 and BA.2 RBD-mACE2 complexes. The BA.1 RBD and complexed hACE2 atomic models are shown in magenta and dark green, respectively. The BA.2 RBD and complexed hACE2 atomic models are shown in purple and light green, respectively.
(D) Atomic model of the BA.2 RBD-mACE2 complex, focused on residues Y501 and H505.
(E) As in (D) but focused on residue R493.
(F) Atomic model of the WT RBD-hACE2, focused on residues N501 and Y505.
(G) As in (H) but focused on residue Q493.
(H) Atomic model of mACE2 from the perspective of a binding RBD. Black labels are mACE2 residues, and gray labels denote the interacting residues in a bound RBD. Gold labels denote the interacting residues in a bound RBD that are mutated in the BA.1 and BA.2 Omicron sub-lineages.