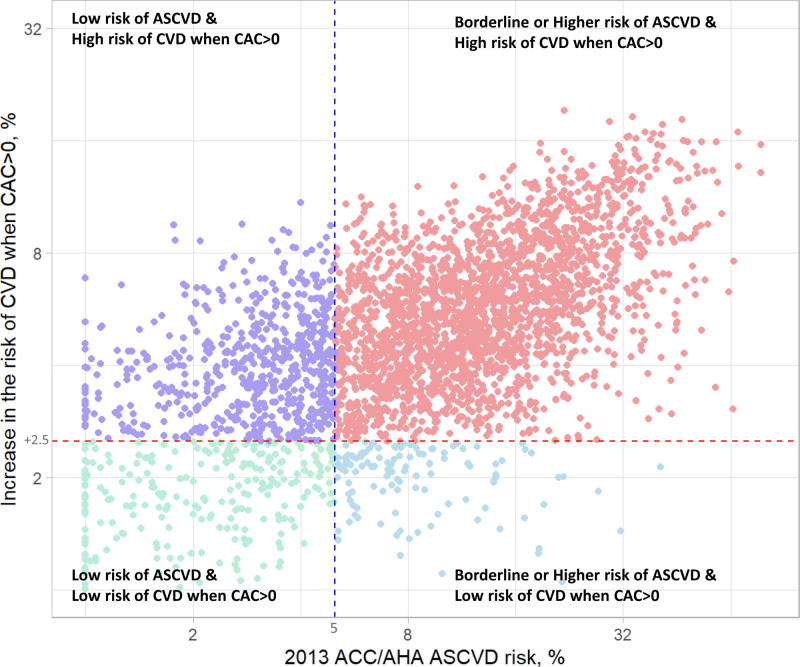
Figure 2.
Association between the 10-year ASCVD risk and the estimated increase in the risk of cardiovascular events when CAC>0 compared to CAC=0. X-axis shows the 10-year ASCVD risk calculated by the 2013 ACC/AHA pooled cohort equations. Y-axis showed the estimated increase in the risk of cardiovascular events when CAC>0 (calculated by the causal forest model). Spearman correlation coefficient and Pearson correlation coefficient between the 10-year ASCVD risk and the estimated increase in the risk of cardiovascular events when CAC>0 were 0.60 (P value <0.001) and 0.61 (P value <0.001), respectively. ASCVD indicates atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; CAC, calcium coronary artery calcium; and CVD, cardiovascular disease.