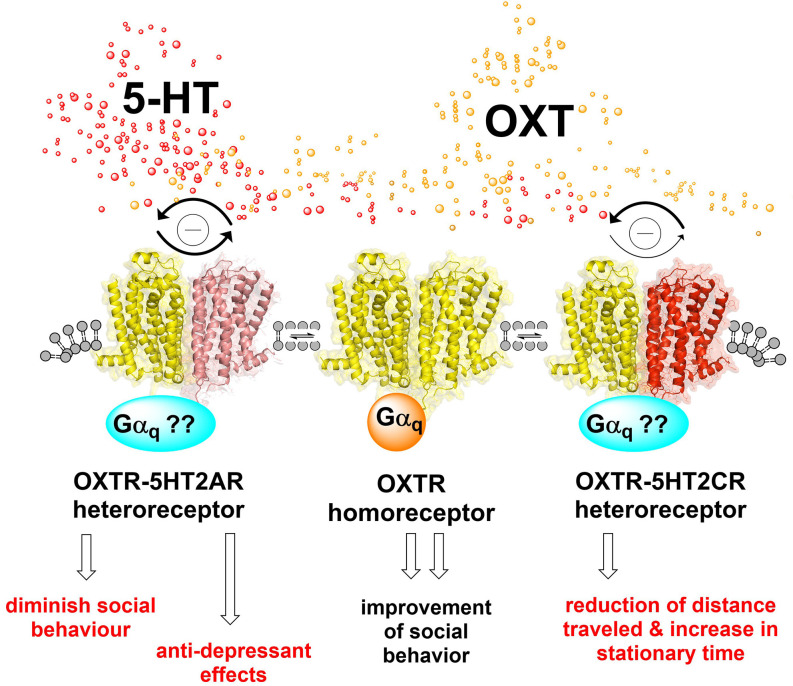
Figure 2.
Oxytocin and serotonin heteroreceptor complexes in the brain. The OXTR-5-HT2AR heteroreceptor complex, shown as a heteroreceptor dimer in the plasma membrane, is found in the left region. The bidirectional antagonistic allosteric receptor-receptor interaction is outlined leading to attenuation of the oxytocin receptor protomer and 5-HT2AR protomer signaling as indicated by the connected two arrows in strong black color. A possible modulation in the G alpha q coupling of this heteroreceptor complex is indicated by the question mark. The 5HT2AR agonist-induced allosteric inhibition of the oxytocin receptor protomer can diminish its increase in social behavior (Froemke and Young, 2021). The Oxytocin receptor protomer (OXTR) can upon activation allosterically inhibit 5-HT2AR protomer signaling and diminish the 5-HT2AR signaling with possible antidepressant effects since 5-HT2AR mediates depressive effects (Borroto-Escuela et al., 2021; Perez de la Mora et al., 2022). The oxytocin homo-receptor complex, shown as a homo dimer, is found in the center of the illustration, coupled to G alpha q. It improves upon the activation of social behavior (Froemke and Young, 2021). The OXTR-5-HT2CR heteroreceptor complex, shown as a heteroreceptor dimer in the plasma membrane, is illustrated on the right side of the figure. The ability of the 5-HT2CR protomer (red) activation to allosterically attenuate the oxytocin receptor protomer G alpha q mediated signaling is substantially stronger (thick arrow) than the ability of the OXTR receptor agonist to allosterically diminish the 5-HT2CR G alpha q signaling (narrow arrow). It may involve differential changes in the degree of alterations in G alpha q coupling and of coupling also to other G proteins. In line with the biochemical results, the 5-HT2CR antagonist strongly enhanced the oxytocin receptor agonist-induced reduction of distance traveled and increase in stationary time (Chruścicka et al., 2021). These findings underline the functional relevance of the OXTR-5-HT2 complexes and their receptor-receptor interactions. Thus, the findings give indications that blockade of 5-HT2CR signaling can enhance oxytocin receptor signaling and produce improvement of social disease.