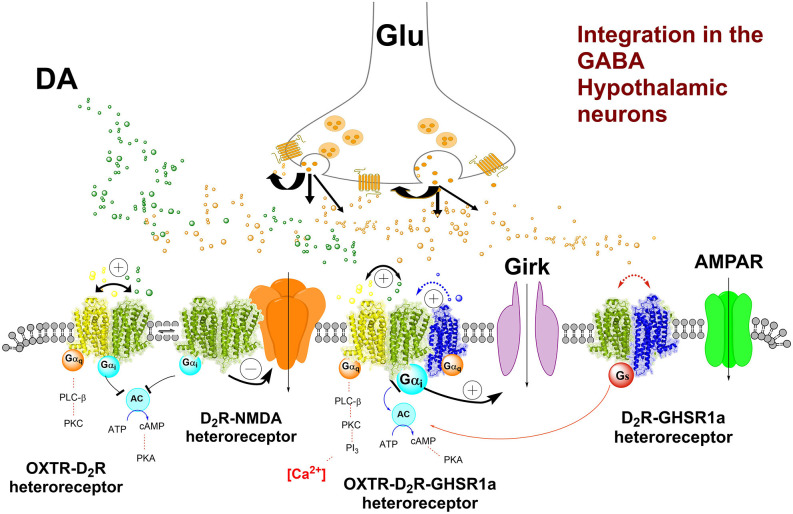
Figure 4.
Hypothesis on the key heteroreceptor complexes in the proposed inhibitory GABA nerve cell population (nucleus) in the lateral hypothalamus projecting to the inhibitory GABA interneurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) controlling meso-limbic DA reward neurons in the VTA. The key higher order heterocomplexes OXTR-D2R-GHS-R1a and the NMDAR-D2R are shown in the plasma membrane of the GABA neurons. The trimeric complex is indicated to be in balance with the OXTR-D2R, OXTR-GHS-R1a, and D2R-GHS-R1a in the plasma membrane. The pharmacology indicates that D2R activation results in the inhibition of food intake related to the inhibition of food reward. The mechanism existing in the trimeric complex may be the D2R-induced opening of the GIRK channels leading to inhibition of the firing of the hypothalamic GABA neurons. Through positive allosteric receptor-receptor interactions the OXTR protomer can enhance the inhibitory D2R signaling. Also, GHS-R1a likely plays a role in this trimeric complex since the removal of the Ghrelin receptor blocks the inhibitions of food intake by the D2R protomer (see text). Thus, it seems likely that the existence of the Ghrelin receptor protomer is necessary for the correct allosteric receptor-receptor interactions to develop by allowing the appropriate conformational changes to develop in this trimericheteroreceptor complex. Thus, the D2R protomer activation can allow the inhibition of the hypothalamic GABA neurons projecting to the VTA GABA interneurons. Also, the potential existence of the NMDAR-D2R hetero complexes in the hypothalamic GABA neurons may help reduce the glutamate drive through D2R protomer-mediated inhibition of the NMDA receptors Thus, this mechanism may also contribute to lowering food-reward. There can exist other types of glutamate receptors located on the hypothalamic GABA neurons that can play an important role like the AMPA receptor and kainate receptors. They can contribute to strong glutamate activation of the hypothalamic. GABA neurons lead to considerable increase of glutamate drive and increased activity in the meso-limbic DA reward neurons by the inhibition of the GABA interneurons and increased food reward can develop also in this way.