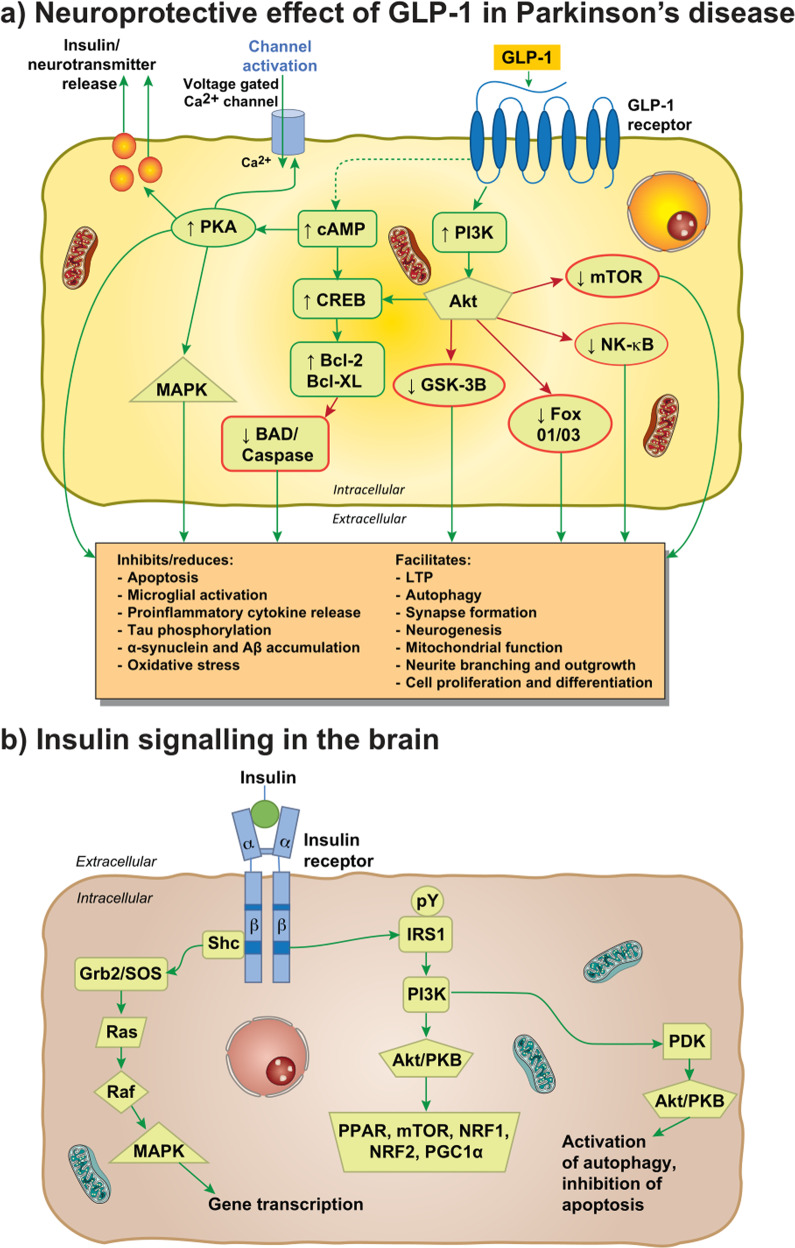
Fig. 2. Neuroprotective effects of GLP-1 and insulin signaling in the brain.
a shows downstream signaling pathways depicting the influence GLP-1 on Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. b Insulin signaling in neurons. b demonstrates the action of insulin in the neuron and activation of downstream pathway. Abbreviations: Bcl-2 B cell lymphoma 2, BAD (Bcl-2) antagonist of death, Bcl-XL B cell lymphoma 2 extra-large, cAMP cyclic AMP, CREB cAMP response element-binding protein, FoxO1/O3 Forkhead box O1/O3, GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide-1, GSK-3B glycogen synthase 3 beta, LTP long-term potentiation, MAPK mitogen-associated protein kinase, mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin, NF-kB nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, PI3K phophoinositide 3-kinase, TNF tumor necrosis factor, Akt/PKB protein kinase B complex, CPD3B cyclic phosphodiesterase 3 beta, Grb2/SOS Growth factor receptor binding protein 2/son of sevenless protein, IRS insulin receptor substrates that get phosphorylated after activation, NRF1 nuclear respiratory factor-1, PGC-1α peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1-α, PDK phosphatidylinosite dependent kinase, PPAR peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor family, Raf regulation of alpha-fetoprotein, Ras rat sarcoma virus peptide, Shc Src homology collagen peptide.