Figure 2. Composite of arterial thrombotic events (A), MI (B), and stroke (C).
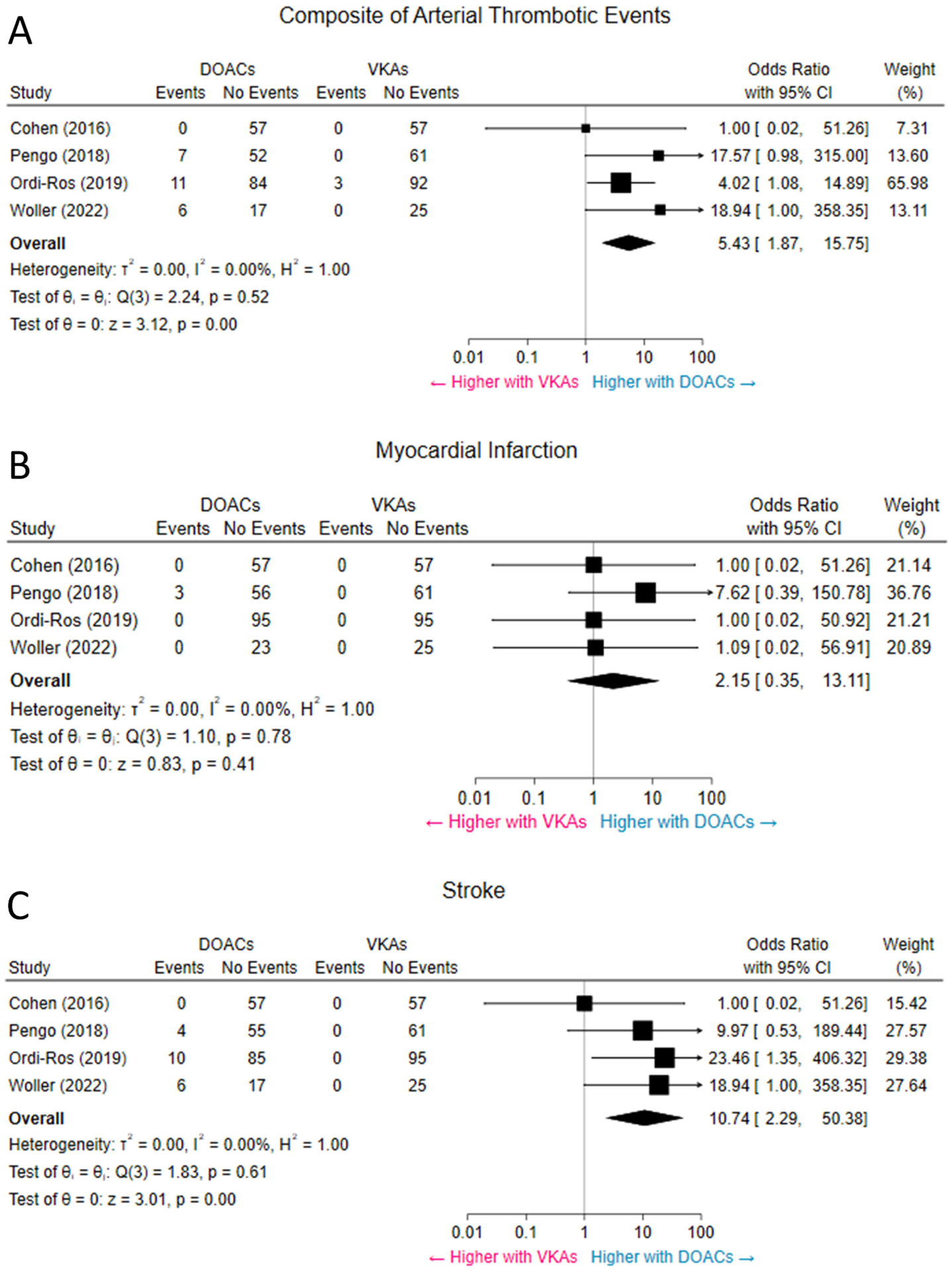
Pooled results revealed higher odds of arterial thrombotic events in patients assigned to DOACs. The rate of stroke was higher with DOACs, while the rate of MI was not significantly different between the two groups. CI = confidence interval; DOACs = direct oral anticoagulants; MI = myocardial infarction; VKAs = vitamin-K antagonists.
