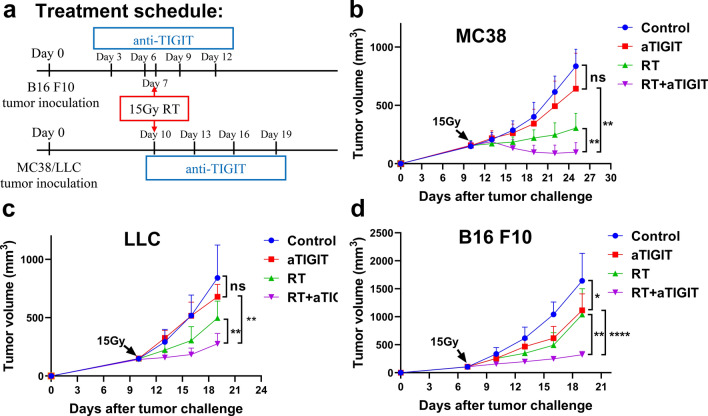
Fig. 3.
RT and anti-TIGIT therapy showed synergistic anti-tumor effects in MC38, LLC and B16 F10 mouse models. A. Diagram depicting the experimental set up including treatment schedules. C57BL/6 mice were inoculated subcutaneously on day 0 with 1 × 10.6 MC38, LLC or B16 F10 cells. MC38 and LLC tumor-bearing mice (n = 5–7mice/group) were treated with one 15 Gy dose 10 days post-tumor inoculation. Mice received 200 ug anti-TIGIT (clone IG9) or isotype IgG intraperitoneally every three days, for a total of four injections. b. Combination therapy greatly delayed MC38 tumor growth compared with individual treatments. c. Combination therapy greatly delayed LLC tumor growth compared with individual treatments. d. Combination therapy greatly delayed B16 F10 tumor growth compared with individual treatments. Anti-TIGIT therapy alone inhibited tumor growth compared with the controls. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001. IgG, immunoglobulin G; NS, not statistically significant; RT, radiotherapy; TIGIT, T cell immunoreceptor with immunoglobulin and ITIM (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif) domains