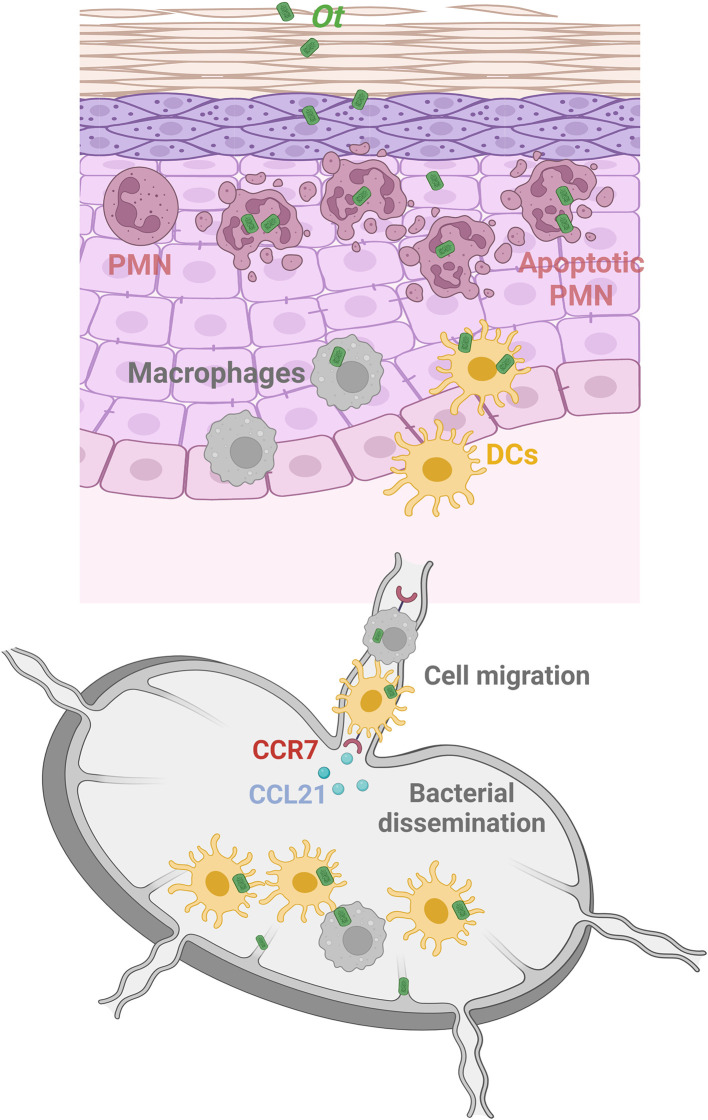
Figure 6.
Graphical illustration of Ot dissemination and innate immune cell responses in an i.d. infection mouse model. Following i.d. infection with Ot, neutrophils are the first responders and rapidly infiltrate the skin. Although neutrophils (purple) efficiently engulf bacteria in the inoculation site, Ot induces neutrophil apoptosis locally, and neutrophils cannot carry Ot into the dLN. Instead, DCs (yellow) and macrophages (gray), which also migrate into the skin for bacterial uptake, are the reservoirs responsible for bacterial dissemination of Ot to the dLN. Notably, they may serve as “Trojan horse” vehicles that carry Ot and migrate into the dLN in a CCR7/CCL21-dependent way to facilitate bacterial replication and dissemination. In addition, lymphatic vessels are also infected by Ot, indicating that lymphatic ECs could be the target cells of Ot replication in the dLN for further bacterial dissemination into visceral organs. This graphical illustration is created with BioRender.com.