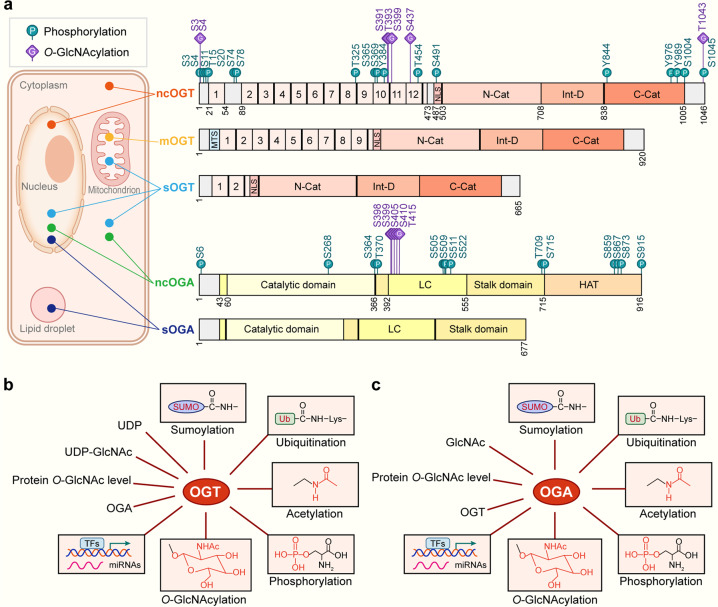
Fig. 2. The molecular structure, localization and regulation of OGT and OGA.
a Structure and localization of OGT and OGA isoforms. All the identified phosphorylation sites are shown as green circles with the letter ‘P’, and O-GlcNAcylation sites are shown as purple squares with the letter ‘G’. The N-terminal region of three OGT isoforms is consisted of TPRs and an NLS. The catalytic region is composed of an N-cat domain, an Int-D, and a C-cat domain. Additionally, mOGT has a typical MTS. These two OGA splicing variants are constituted by a catalytic domain in the N-terminal region and two stalk domains (including N-terminal and C-terminal) and two LC regions, but they differ in a pseudo-HAT domain. The localization of ncOGT and ncOGA mainly concentrates in the cytoplasm and nucleus. mOGT gathers in the mitochondrion, and sOGT is present in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and mitochondrion. sOGA is centered in the nucleus and lipid droplet. b Regulation of OGT. OGT is modulated at several aspects containing HBP substrate availability such as UDP and UDP-GlcNAc. The intracellular protein O-GlcNAc level and the counterpart magnitude of OGA can regulate OGT in a feedback style. OGT can be regulated through TFs and miRNAs at the transcriptional level. Post-translational modifications e.g., O-GlcNAcylation, phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and sumoylation can also regulate OGT. c Regulation of OGA. OGA is regulated by various factors containing feedback inhibition by intracellular GlcNAc level. The intracellular protein O-GlcNAc level and the counterpart magnitude of OGT can regulate OGA. OGA can be regulated through TFs and miRNAs at the transcriptional level. Post-translational modifications by O-GlcNAcylation, phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and sumoylation can also regulate OGA. OGT O-GlcNAc transferase, OGA Protein O-GlcNAcase, UDP-GlcNAc Uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine, TPRs Tetratricopeptide repeats, NLS Nuclear localization signal, N-cat N-terminal catalytic domain, Int-D Intervening sequence, C-cat C-terminal catalytic domain, MTS Mitochondrial targeting sequence, LC Low complexity, pseudo-HAT Pseudohistone acetyl transferase, TFs Transcription factors, miRNAs MicroRNAs, ncOGT Nucleocytoplasmic OGT, mOGT Mitochondrial OGT, sOGT Short OGT, ncOGA Nucleocytoplasmic OGA, sOGA Short isoform OGA. The databases https://glygen.org/, https://www.uniprot.org/, and https://research.bioinformatics.udel.edu/iptmnet/ are used to search for known modification sites.