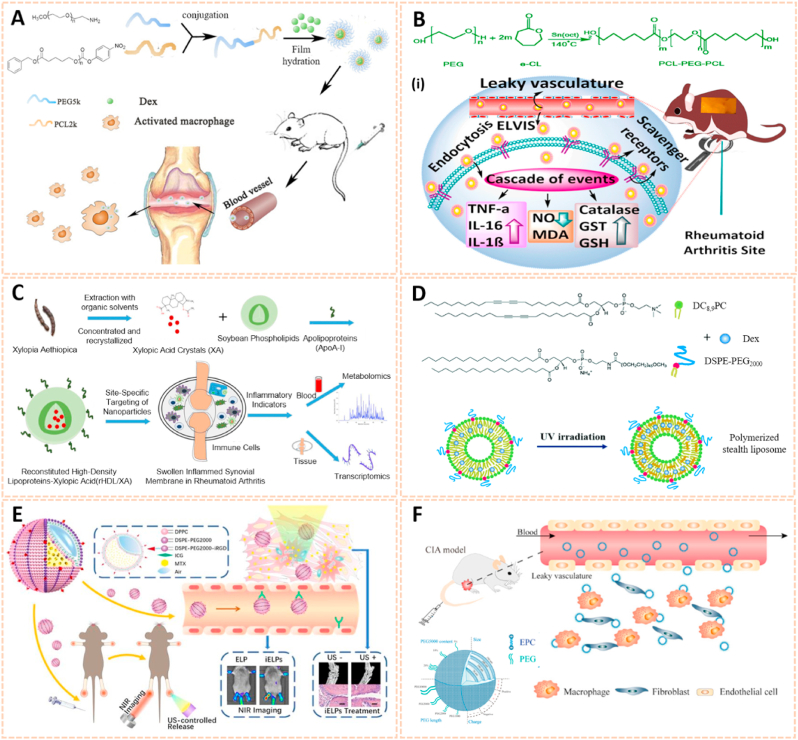
Fig. 14.
Polymer and liposomes-based nanomaterials as passive targeting drug carriers. A) Schematic preparation and therapy of Micelles-Dex [167]. The image reproduced with the permission from Elsevier B.V. B) Reaction scheme for the synthesis of PCL-PEG-PCL. (i) Schematic mechanisms of MTX nanomicelles-based hydrogel against RA [138]. The image reproduced with the permission from American Chemical Society. C) Schematic summary of the entire study [168]. The image reproduced with the permission from Elsevier Ltd. D) Chemical structure of DC8,9PC, DSPE-PEG2000 and schematic of polymerized stealth liposomes with loaded Dex [171]. The image reproduced with the permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry. E) The schematic illustration of iELPs and the mechanism of NIR fluorescence imaging and treatment [172]. The image reproduced with the permission from Ivyspring. F) Schematic of the characteristics and RA targeting effect of liposomes in the inflammatory microenvironment of RA. Liposomes were mainly taken up by macrophages and fibroblasts after entering the joint cavity through the leaky vasculature. Fewer liposomes were taken up by endothelial cells [37]. The image reproduced with the permission from American Chemical Society.