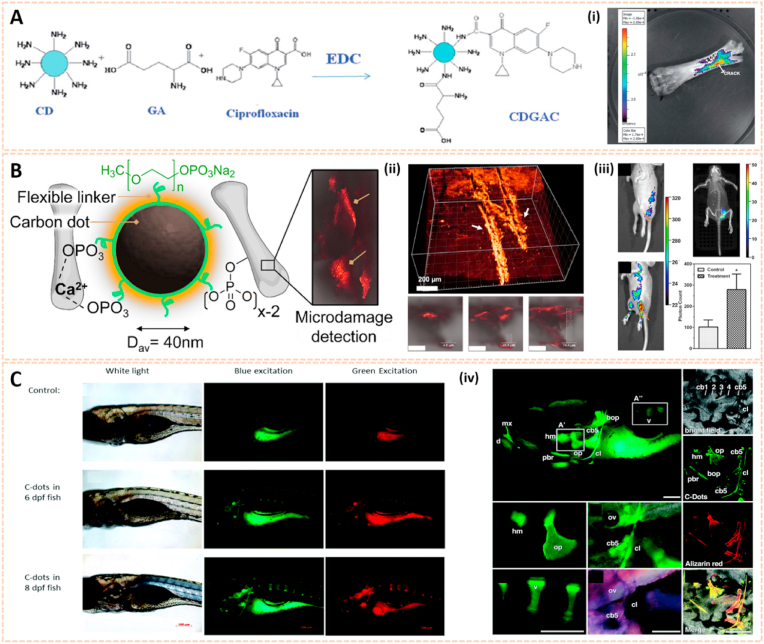
Fig. 3.
Quantum dots for biomedical imaging. A) Conjugation of GA and ciprofloxacin onto CDs. (i) Bone crack detection (marked) by CDGAC imaged with the IVIS system [51]. The images reproduced with the permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry. B) Monodentate ligand can come close together on the CD surfaces to chelate Ca2+ which gets exposed abundantly at the site of the microcrack. The fluorescence from the CD can be utilized for the detection of bone microcracks. (ii) 3D confocal image of the NPs residing in the bone microcracks (λex = 488 nm). (iii) In vivo fluorescence of monophosphonated CDs in the tibia with distinct site enhancement in the signal to background intensity [42]. The images reproduced with the permission from American Chemical Society. C) Zebrafish images under white light, blue light excitation and green light excitation 6- and 8-days post fertilization (dpf) with 5 nL injection of 1 μg μL-1 C-dots. (iv) C-Dots deposit with high affinity and specificity on ossified bones [53]. The images reproduced with the permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry.