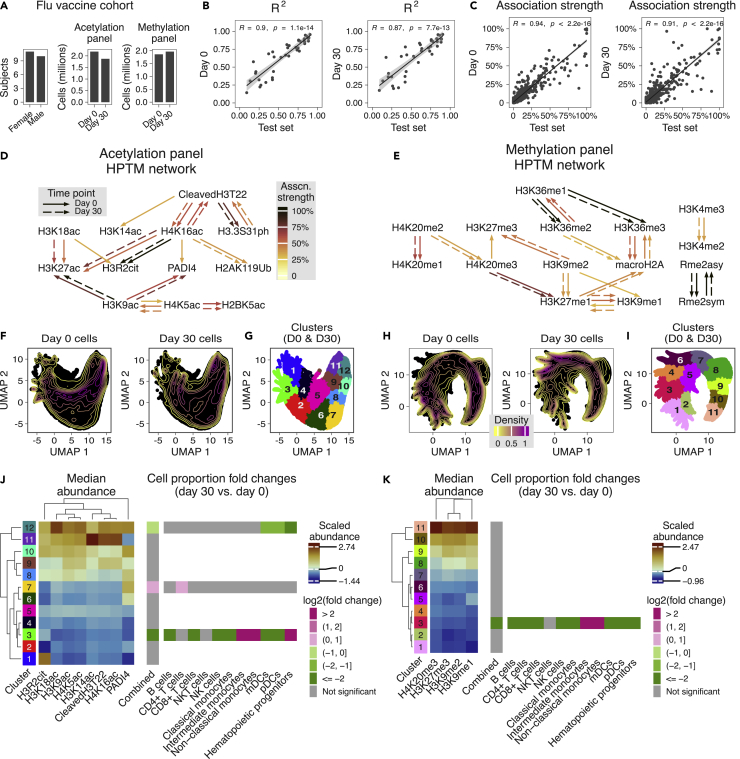
Figure 4.
Inferred HPTM networks identify changes in HPTM associations following influenza vaccination
(A) Summary of Flu vaccine cohort.
(B) Comparison of NP task 3 R2 between Flu vaccine cohort samples and test set. Each dot represents a unique HPTM (n = 38 per time point).
(C) Comparison of HPTM association strength between Flu vaccine cohort samples and test split. Each dot represents a unique pair of HPTMs (n = 684 per time point). T-test was used to compute the significance of the Pearson correlation coefficient.
(D and E) (D) Acetylation and (E) methylation panel HPTM networks from Day 0 and Day 30 time points. Arrows go from input to output HPTM.
(F) UMAP visualization of cells in acetylation panel based on HPTMs that change in the association network (cleaved H3T22, H3K14ac, H4K16ac, PADI4, H3K18ac, H3R2cit, H2K9ac, and H4K5ac). Each time point contains 250,000 cells sampled randomly.
(G) PhenoGraph clustering of cells in acetylation panel. Clustering was performed in the UMAP space and used 25,000 cells per time point randomly sampled from those used for UMAP.
(H) UMAP visualization of cells in methylation panel based on HPTMs that change in the association network (H4K20me3, H3K27me3, H3K9me2, and H3K9me1). Each time point contains 250,000 cells sampled randomly.
(I) PhenoGraph clustering of cells in methylation panel. Clustering was performed in the UMAP space and used 25,000 cells per time point randomly sampled from those used for UMAP.
(J and K) Median abundance of HPTMs and fold changes in sample-wise cell proportion between Day 30 and Day 0 in the (J) acetylation and (K) methylation panels. All cells from all samples were used to calculate the medians and proportions. FDR-adjusted Wilcoxon test was used to compute the significance of differences in proportion means across groups (n = 21 subjects per time point).
See also Figures S8 and S9.