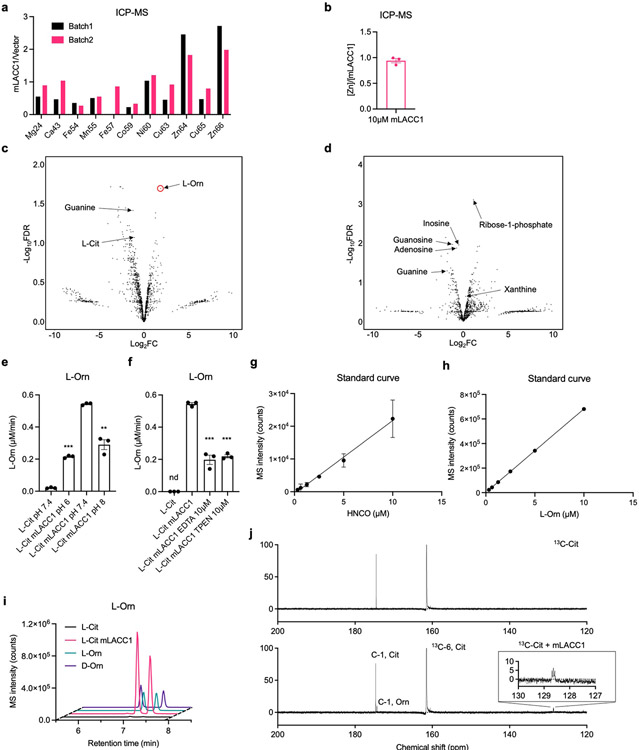
Extended Data Fig. 1.
In vitro biochemical analysis of isolated LACC1 variants. a, ICP-MS assays showed the enrichment of Zn64 and Zn66 isotopes in recombinant mLACC1 relative to vector control. b, A quantitative ICP-MS assay for Zn showed the average Zn:mLACC1 ratio as 0.94, suggesting a 1:1 ratio in the isolated enzyme. c-d, Volcano plots from UPLC-QTOF-MS experiments showing the fold change (FC) (substrate with mLACC1 versus substrate with heat inactivated mLACC1) and false discovery rate (FDR) values collected in positive ion mode (c) and negative ion mode for the specific detection of ribose-1-phosphate (d). e, Rates of L-Orn production in enzymatic assays at different pH conditions. f, Rates of L-Orn production in enzymatic assays with the supplementation of EDTA or TPEN in the reaction buffer. g, The standard curve used for quantifying L-Orn in enzymatic assays. h, The standard curve used for quantifying 2-aminobenzoate-HNCO carbamoylation products in enzymatic assays. i, The LC-MS trace of 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrophenyl-5-L-alanine amide (FDAA, Marfey’s reagent)-coupled L-Orn in enzymatic assays, supporting the stereoconfiguration. j, Expanded view 13C-NMR spectroscopic data of LACC1 reaction using 6-13C1-L-Cit as substrate, showing L-Orn and HNCO as major products. The mean and SEM (error bars) are derived from three biological replicates (n = 3). Statistical significance (two-tailed t-test) compared to control (Ctrl): *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; nd, not detectable.