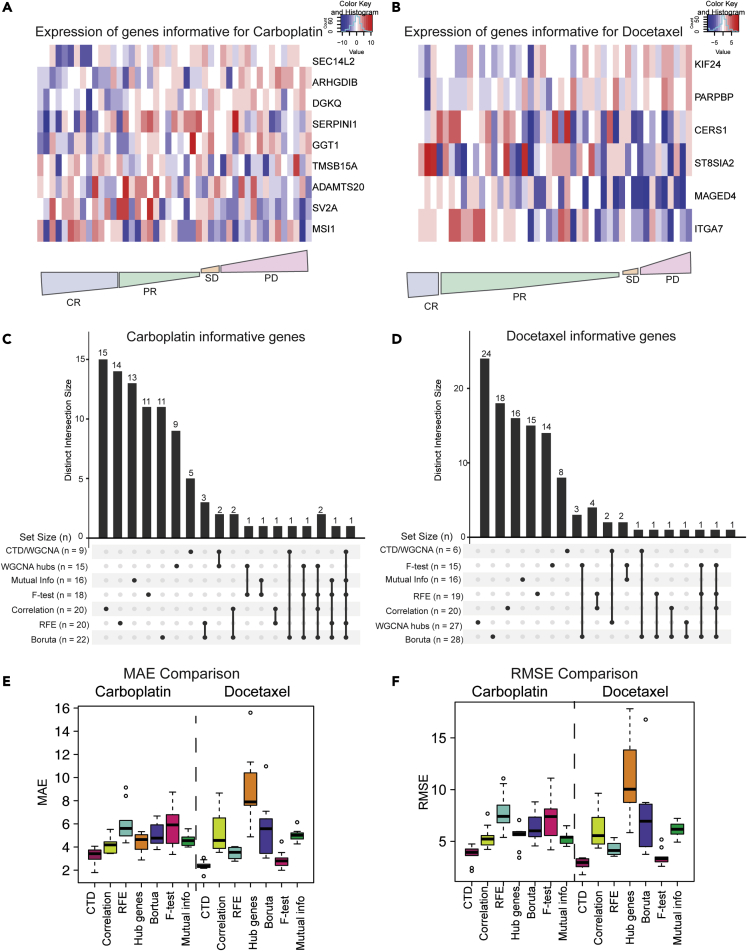
Figure 5.
CTD outperforms other feature selection methods when selecting informative genes and is predictive in our PDX cohort
(A) Heatmap of informative genes for carboplatin across all PDXs from most responsive (left) to most resistant (right). CR, complete response; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease; PD, progressive disease.
(B) Heatmap of informative genes for docetaxel across all PDXs from most responsive (left) to most resistant (right). CR, complete response; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease; PD, progressive disease.
(C) Overlap between genes predicted to be informative for carboplatin by commonly used feature selection methods visualized with an UpSet plot.
(D) Overlap between genes predicted to be informative for docetaxel by commonly used feature selection methods visualized with an UpSet plot.
(E) MAE comparison of 4 different methods (red = CTD/WGCNA approach, lime green = correlation, turquoise = recursive feature extraction, orange WGCNA hub genes, purple = Boruta, pink = F-test, green = mutual information regression).
(F) RMSE comparison of 4 different methods (red = CTD/WGCNA approach, lime green = correlation, turquoise = recursive feature extraction, orange WGCNA hub genes, purple = Boruta, pink = F-test, green = mutual information regression).