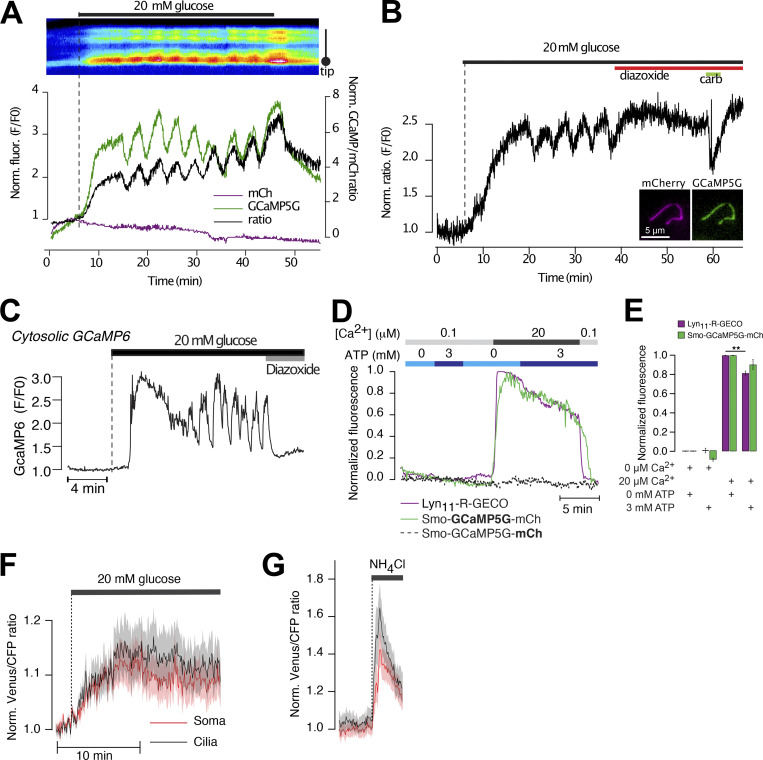
Figure S7.
Ca2+-independent changes in GCaMP5G fluorescence induced by 20 mM glucose. (A) Ratiometric recording (black) of GCaMP5G (green) and mCherry (magenta) fluorescence from a mouse islet cell cilium expressing Smo-GCaMP5G-mCh. Notice that glucose causes an immediate increase in GCaMP5G fluorescence but is without effect on mCherry fluorescence. (B) Ratiometric (GCaMP5G/mCherry) recording from the cilium of a mouse islet cell exposed to 11 mM glucose followed by the addition of hyperpolarizing diazoxide (250 μM) and carbachol (10 μM). Notice that the addition of diazoxide suppresses the glucose-induced Ca2+ oscillations but does not bring the GCaMP5G/mCh ration back to resting levels. (C) TIRF microscopy recording of GCaMP6 fluorescence from a transgenic mouse islet β-cell expressing GCaMP6 under control of the insulin promoter. The islet was exposed to a step increase in the surrounding glucose concentration, from 3 to 20 mM, followed by addition of the hyperpolarizing agent diazoxide. Notice that in contrast to Smo-GCaMP5G-mCh (see Fig. S2 A), glucose does not cause an immediate increase in GCaMP fluorescence, and the glucose-induced increase in GCaMP fluorescence is suppressed to resting levels in the presence of diazoxide. (D) Fluorescence changes from α-toxin–permeabilized MIN6 cells expressing Smo-GCaMP5G-mCh (green/dashed black) or plasma membrane-anchored R-GECO (Lyn11-R-GECO; magenta) following exposure to intracellular-like buffers containing the indicated Ca2+ and ATP concentrations. (E) Quantifications of GCaMP5G and Lyn11-R-GECO fluorescence changes in permeabilized cells exposed to the indicated intracellular buffers (n = 13–16 cells, ** P < 0.01, two-tailed paired Student’s t test). (F) Venus/CFP ratio changes in the cell body (red) and cilia (black) of MIN6 cells expressing cilia-targeted 5HT6-Venus-CFP and exposed to an increase in the surrounding glucose concentration from 3 to 20 mM (means ± SEM of 21 cells). (G) Venus/CFP ratio changes in the cell body (red) and cilia (black) of MIN6 cells expressing cilia-targeted 5HT6-Venus-CFP and exposed to 20 mM NH4Cl, which causes strong alkalinization of the cytosol (means ± SEM of 21 cells).