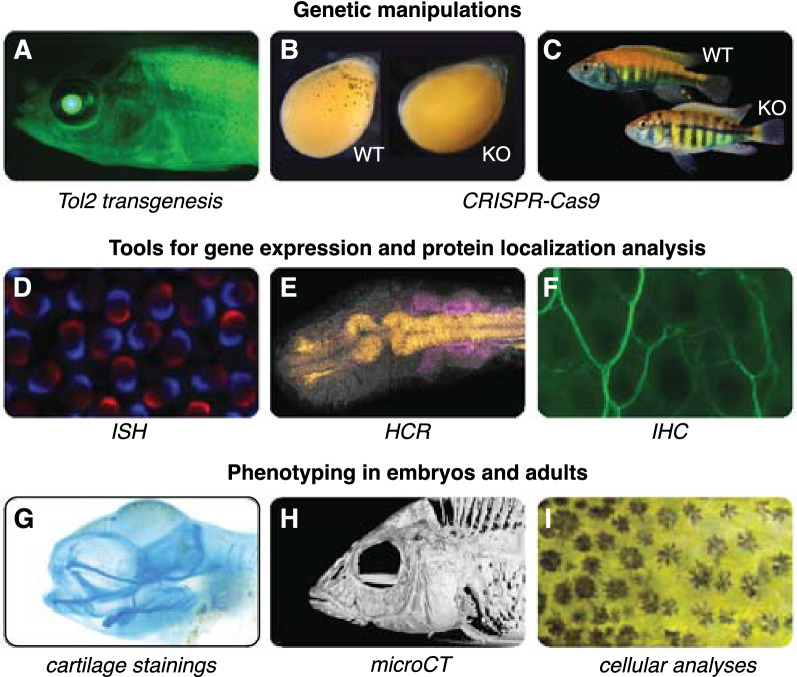
Fig. 8.
Experimental and phenotyping approaches in cichlids. (A–I) A wide variety of methodological approaches, including methods available in cichlid fishes that are comparable to other teleost fish model systems. These include methods for genetic manipulations (A–C), gene expression and protein localization (D–F), and phenotyping in embryos and adults G, H. A Transgenic cichlid fish of the species Astatotilapia burtoni constitutively expressing GFP under the elongation factor 1 alpha, ef1a promotor. B Stable CRISPR–Cas9 knockout of the pigmentation gene oculocutaneous albinism II, oca2 in Astatotilapia calliptera leading to loss of melanin in melanophores. C Transient CRISPR–Cas9 knockout of the “stripe gene” agrp2 in Pundamilia nyererei, resulting in the appearance of horizontal stripe patterns in this usually non-striped species. D Fluorescent in situ hybridization (ISH) for rhobdopsin 2b, rh2b and longwave-sensitive (lws) opsin in the Malawi cichlid Maylandia zebra. E In situ DNA-hybridization chain reaction (HCR) for pax7 (orange) and SRY-box transcription factor 10, sox10 (magenta) in Rhamphochromis sp. ‘chilingali’. F Immunohistochemistry (IHC) for nerve fibers on scales of Melanochromis auratus using an acetylated tubulin antibody. G Cartilage staining of an embryo of Tropheops sp. ‘mauve’. H MicroCT 3D visualization of Aulonocara stuartgranti. I Microscopic analysis of melanophore development and patterning in an embryo of the Lake Victoria basin cichlid Haplochromis latifasciatus. Photo credits: Scott Juntti (A), Joel Elkin / Bethan Clark (B), Brian Dalton / Karen Carleton (D), Aleksandra Marconi (E, G), Duncan Edgley (H), Jan Gerwin (I)