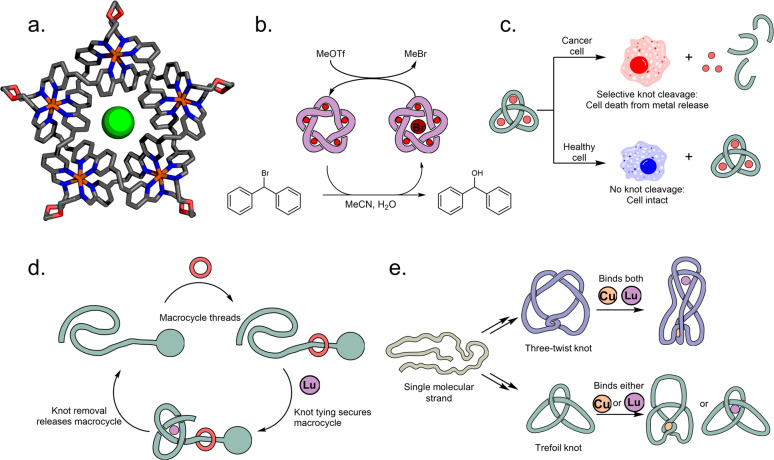
Fig. 2. Functions of molecular knots.
a X-ray crystal structure of a molecular pentafoil knot that can bind halide ions strongly within its central cavity. b Molecular knots performing catalysis, here illustrated by a pentafoil knot binding bromide and catalysing a hydrolysis reaction (MeOTf is converted to gaseous MeBr to complete the catalytic cycle and enable turnover). c Trefoil knots act as delivery agents of metals (CuII, FeII, MnII, ZnII, CdII) that selectively kill cancer cells. d A molecular knot can be used to perform mechanical functions at the nanoscale, such as securing and releasing a macrocycle. e Several different knots can be tied from the same molecular strand. The resulting topoisomeric three-twist and trefoil knots possess different metal binding properties.