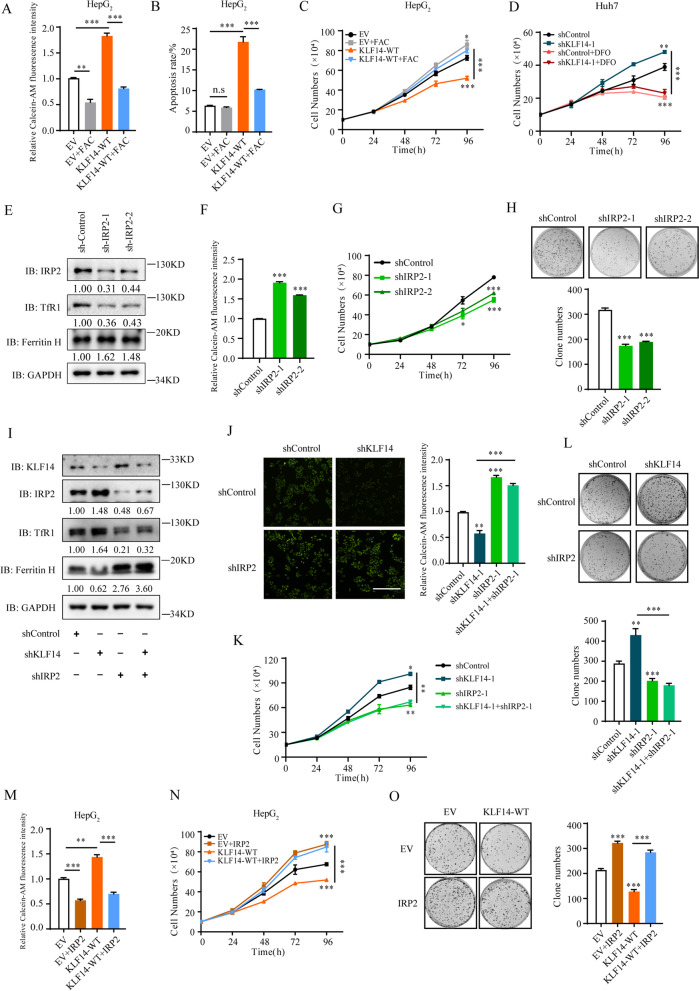
Fig. 4.
KLF14-mediated inhibition of HCC cells growth is dependent on iron and IRP2. A Relative cellular LIP content of HepG2 cells with KLF14 overexpressed were measured in standard media or media supplemented with 100 μM ferric ammonium citrate (FAC). B Cell apoptosis caused by KLF14 overexpression were reduced with FAC treatment. C Cell growth curve of HepG2 cells with KLF14 overexpressed in standard media or media supplemented 100 μM FAC for 4 days. D Cell growth curve of HepG2 cells with KLF14 silenced in standard media or media supplemented 100 μM DFO for 4 days. E Protein levels of IRP2, TfR1 and FH in IRP2 silenced cells were examined by western blotting. F Relative cellular LIP content of IRP2 silenced cells. G Cell growth curve of IRP2 silenced HepG2 cells. H Colony formation ability of HepG2 cells with IRP2 silenced. I Protein levels of IRP2, TfR1 and FH in KLF14 and/or IRP2 silenced cells were examined by western blotting. J The relative cellular LIP contents in KLF14 and/or IRP2 silenced cells were measured at 24 h (left panel) and 36 h (right panel). K Cell growth curve of KLF14 and/or IRP2 silenced HepG2 cells. L Colony formation ability of HepG2 cells with KLF14 and/or IRP2 silenced. M Relative cellular LIP content of KLF14 and/or IRP2 overexpressed cells. N Cell growth curve of KLF14 and/or IRP2 overexpressed HepG2 cells. O Colony formation ability was restored when IRP2 was overexpressed in KLF14 overexpressed cells. All results are presented as means ± SD from three independent experiments. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s T-tests were performed. n.s, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001