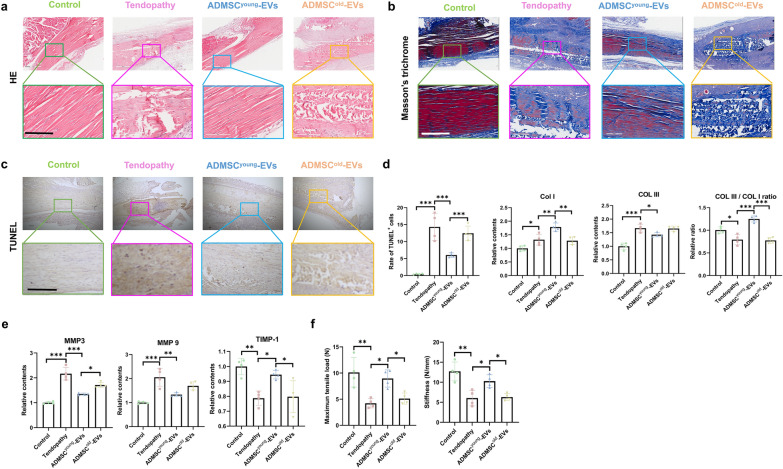
Fig. 4.
ADMSCyoung-EVs, but not ADMSCold-EVs, alleviated the pathological structural, functional and biomechanical properties in tendinopathy. a H&E staining of tendon tissues in the control, tendinopathy, tendinopathy with ADMSCyoung-EVs and tendinopathy with ADMSCold-EVs treatment groups 4 weeks after surgery. Scale bar = 200 μm, n = 4. b Masson’s trichrome staining of tendon tissues of the control, tendinopathy, tendinopathy with ADMSCyoung-EVs and tendinopathy with ADMSCold-EVs treatment groups 4 weeks after surgery. The collagen fibers were stained red, and the collagen matrix disruptions were stained blue. Scale bar = 200 μm, n = 4. c TUNEL assay of the control, tendinopathy, tendinopathy with ADMSCyoung-EVs and tendinopathy with ADMSCold-EVs treatment group 4 weeks after surgery. Scale bar = 200 μm. The rate of TUNEL-positive cells was analyzed, n = 4. d The relative expression of Col I and Col III and the Col III/Col I ratio by ELISAs of tendon tissues of the control, tendinopathy, tendinopathy with ADMSCyoung-EVs and tendinopathy with ADMSCold-EVs treatment groups 4 weeks after surgery, n = 4. e The relative expression of MMP3, MMP9 and TIMP-1 by ELISAs of tendon tissues of the control, tendinopathy, tendinopathy with ADMSCyoung-EVs and tendinopathy with ADMSCold-EVs treatment groups 4 weeks after surgery. f The biomechanical properties, including the maximum tensile load and stiffness of tendon tissues of the control, tendinopathy, tendinopathy with ADMSCyoung-EVs and tendinopathy with ADMSCold-EVs treatment groups 4 weeks after surgery, n = 4. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (*: P < 0.05; **: P < 0.01; ***: P < 0.001)