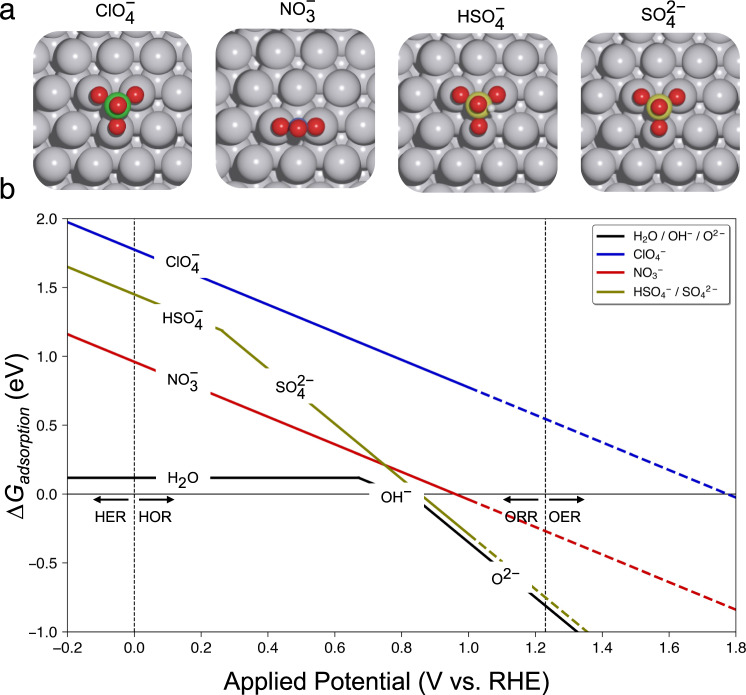
Fig. 3. Potential dependent anion adsorption on Pt(111) surface.
a The most stable adsorption configurations of anions on the Pt(111) surface. Color coded: O: red, H: white, Cl: green, N: blue, and S: olive. b The adsorption free energies of the anions, ΔGadsorption(An−) (eV), on the Pt(111) surface as a function of applied potential (V vs. RHE). The colored dashed lines qualitatively shows the trends in ΔGadsorption(An−) at higher potentials relevant for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER). Since the Pt(111) surface undergoes surface oxidation at these high potentials, we further calculated ΔGadsorption(An−) trends on a PtO2(110) surface as shown in Supplementary Fig. 5 and Supplementary Table 4. Anion species color-coded: black (H2O/OH–/O2–), blue (), red (), and olive (). HER/HOR, and ORR stand for hydrogen evolution/oxidation reaction and oxygen reduction reaction, respectively.