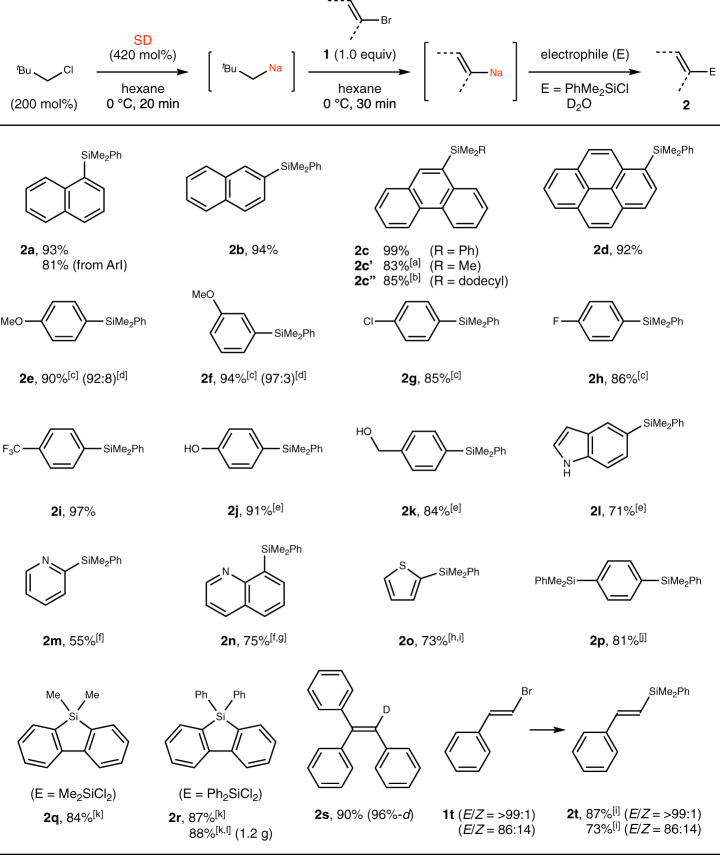
Fig. 3. Halogen–sodium exchange between aryl and alkenyl halides and neopentylsodium.
Neopentylsodium prepared in situ from neopentyl chloride (200 mol%) and SD (420 mol%) was reacted with organic halides (1, 0.25 mmol) in hexane (2.0 mL) at 0 °C, followed by addition of R3SiCl (1.2 equiv), R2SiCl2 (2.0 equiv), or D2O (1.0 mL) as an electrophile. Yields determined by isolation are shown unless otherwise noted. Deuterium content was determined by 1H NMR. aMe3SiCl (1.2 equiv). b(Dodecyl)Me2SiCl (1.2 equiv). cExchange reaction at –40 °C for 10 min. dRatio of monosilylated and disilylated products were determined by 1H NMR. eNeopentyl chloride (300 mol%), SD (630 mol%), hexane (2.5 mL), and PhMe2SiCl (3.0 equiv); after reaction, the concentrated crude mixture was reacted with K2CO3 (5.0 equiv) in MeOH (3.0 mL) for 1 h. fExchange reaction at –78 °C. gTHF (0.80 mL) was used as a co-solvent. hNeopentyl chloride (120 mol%) and SD (250 mol%). iExchange reaction for 10 min. jNeopentyl chloride (300 mol%), SD (630 mol%), hexane (2.5 mL), and PhMe2SiCl (3.0 equiv). kNeopentyl chloride (340 mol%), SD (710 mol%), hexane (2.5 mL), and R2SiCl2 (2.0 equiv). l4.0 mmol scale. SD sodium dispersion, tBu tert-butyl, Ph phenyl, Me methyl, MeO methoxy.