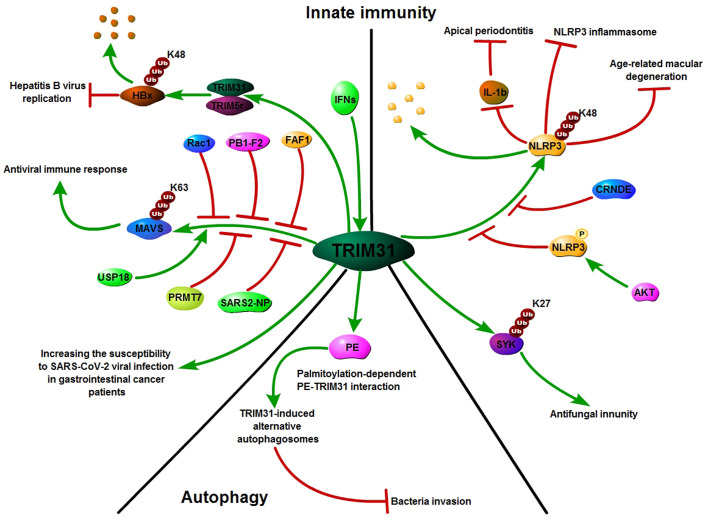
Figure 4.
TRIM31: Growing influence in innate immunity and autophagy. TRIM31 plays an important role in innate immunity; TRIM31 interacts with MAVS and catalyzes the Lys63 (K63)-linked polyubiquitination of MAVS to promote the formation of prion-like MAVS aggregates after viral infection. USP18 promotes TRIM31-mediated K63-linked MAVS polyubiquitination, while PB1-F2, Rac1, PRMT7, SARS2-NP and FAF1 inhibit TRIM31-mediated K63-linked MAVS polyubiquitination. TRIM31 directly binds to NLRP3 and promotes K48-linked polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of NLRP3. AKT and CRNDE decreased TRIM31-mediated NLRP3 ubiquitination. Alongside its emerging role in innate immunity, TRIM31 is also known to be involved in autophagy.