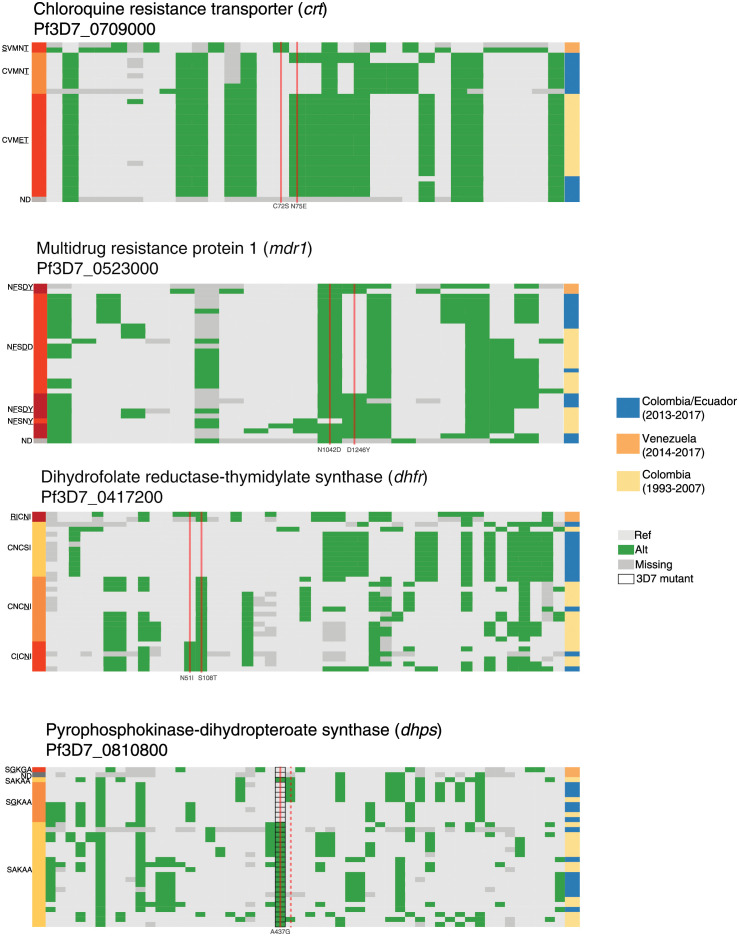
Fig 6. Haplotypes surrounding known drug resistance mutations in crt, mdr1, dhfr, and dhps show varying degrees of diversity.
Plots display segregating SNPs within the 30-kb flanking regions around mutations of interest within four genes involved in antimalarial drug resistance. One high-coverage sample from each clonal cluster is displayed (rows). SNP positions were removed if they were within five nucleotides of a called indel or if they displayed a high rate of heterozygous calls within monoclonal samples (Materials and Methods). Calls are colored based on matching (light grey) or mismatching (green) the 3D7 reference. Calls are marked as missing (dark grey) if they were heterozygous or had fewer than five reads. Black outlines at alleles coding for dhps position 437 indicate that 3D7 contains the A437G mutation; wildtype calls are therefore green at this position. Nonsynonymous mutations of interest are depicted with a solid vertical red line. One synonymous mutation at codon 540 in dhps is depicted with a dashed vertical red line. Represented genes and downstream codon changes are (top to bottom): crt (72 and 75); mdr1 (1042 and 1246); dhfr (50, 51 and 108); and dhps (437 and a synonymous mutation coding for 540). S2 Table lists the mutations detected in the clonal clusters.