Extended Data Fig. 7 |. Characterization of HLA class I restricted CD4+TILs.
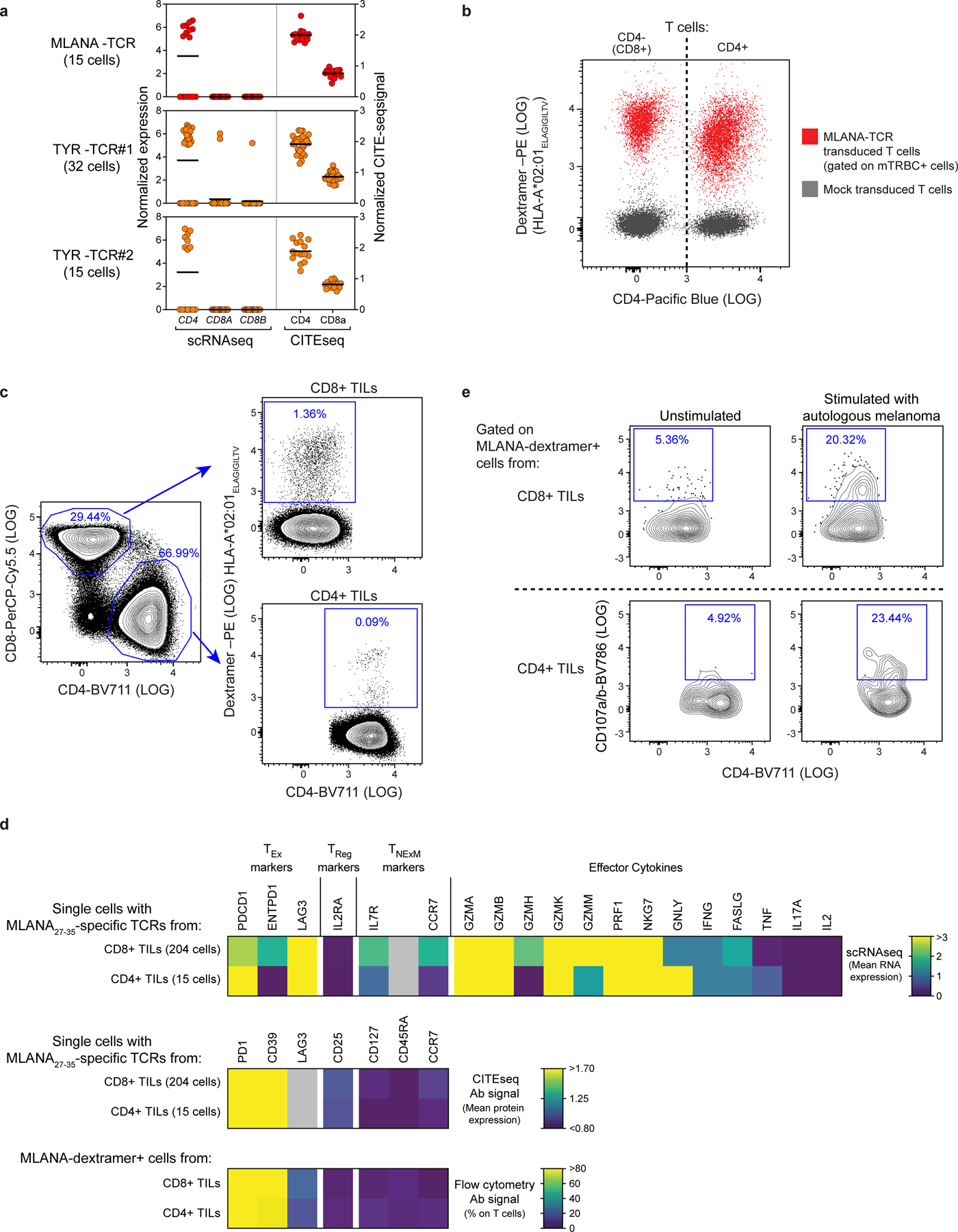
a, Levels of CD4/CD8 transcripts (left, detected by scRNA-seq) or surface proteins (right, detected by CITE-seq) expressed by single cells with CD4+HLA class I restricted TCRs specific for MLANA (n = 1) or TYR (n = 2) isolated from Pt-A. The data indicate that the 3 clonotype families belong to CD4+TILs, despite their reactivity to HLA class I restricted epitopes. b, Flow cytometric plot depicting peptide-HLA binding of T cells transduced with MLANA27–35- specific TCR (red), isolated in CD4+TILs from Pt-A. Transduced T cells comprising CD4+ and CD8+ (CD4−) lymphocytes were stained using HLA-A*02:01 dextramers loaded with MLANA26–35 heteroclitic peptide (ELAGIGILTV). Untransduced T cells (grey) are shown as control. The similar level of binding exhibited by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells demonstrates that tested HLA class I TCR act independently from CD4/CD8 co-stimulation. c, Flow cytometry tracing of MLANA-specific HLA class I restricted CD4+ T cells in Pt-A TILs. Plots depict identification of CD4+ or CD8+ cells within CD3+ TILs from Pt-A (left) and binding to HLA-A*02:01 dextramers loaded with MLANA26–35 heteroclitic peptide among CD4+ or CD8+ TILs (right). Frequencies of each population are provided (blue), demonstrating reliable detected of HLA class I restricted CD4+TILs. d, Phenotype of MLANA-specific HLA class I restricted CD4+TILs from Pt-A. Heatmaps show transcript levels detected by scRNA-seq (top), surface protein expression measured by CITE-seq (middle) or flowcytometry (bottom) for CD4+ T cells with TCRs specific for HLA-A*02:01- MLANA26/27–35 complexes. As comparison, the same analysis was performed on CD8+ TILs specific for the same antigen-HLA (as identified in13) or detected by flow cytometry (as depicted in panel c). Markers detected with all the 3 technologies are shown (exhaustion markers: PD-1, CD39, LAG3; regulatory marker: CD25; memory markers: CD127, CD45RA, CD127). For scRNA-seq (top) transcripts related to effector molecules are reported. Grey color: values not available. This analysis shows that HLA class I restricted CD4+TILs specific for MLANA display an exhausted and cytotoxic phenotype similar to the one of CD8+ TILs. e, Cytotoxicity of HLA-class I-restricted CD4+TILs. Degranulation (CD107a/b upregulation) measured in vitro on MLANA-specific HLA-A*01:02 restricted CD4+ or CD8+ T cells, identified in TILs from Pt-A as depicted in c. Cells were cultured in the absence (left) or presence (right) of autologous melanoma for 6 h. HLA-class I restricted CD4+TILs specific for MLANA antigen (bottom raw) exhibited degranulation levels comparable to those observed for CD8+ counterparts (top raw), demonstrating their ability to mediate cytotoxicity.
