Figure 5. Conformational changes of STAT1 and STAT2 complexes.
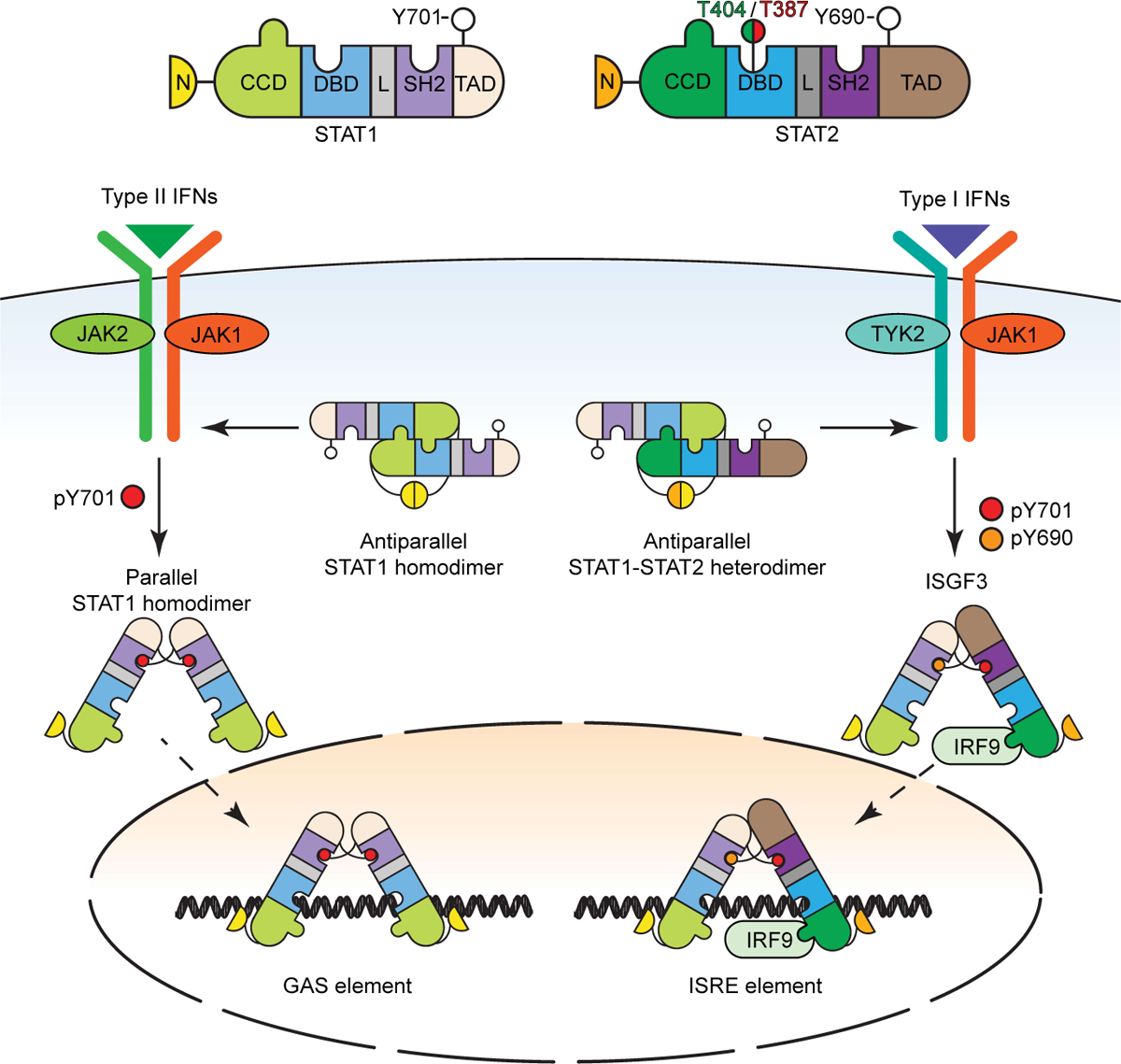
See Figure 4 for definitions of the STAT structural domains. Structural insights indicate that the STAT1 homodimer and the STAT1:STAT2 heterodimer each adapt two conformations, termed parallel and antiparallel. The parallel dimers are stabilized by interactions between the SH2 domains and the phosphorylated tyrosine residues, whereas the antiparallel dimers are stabilized by ND interactions. In addition to the tyrosine phosphorylations, two newly discovered phosphorylations of T387 and T404 of STAT2 regulate U-STAT1:U-STAT2 heterodimer stability. See the text for details.
