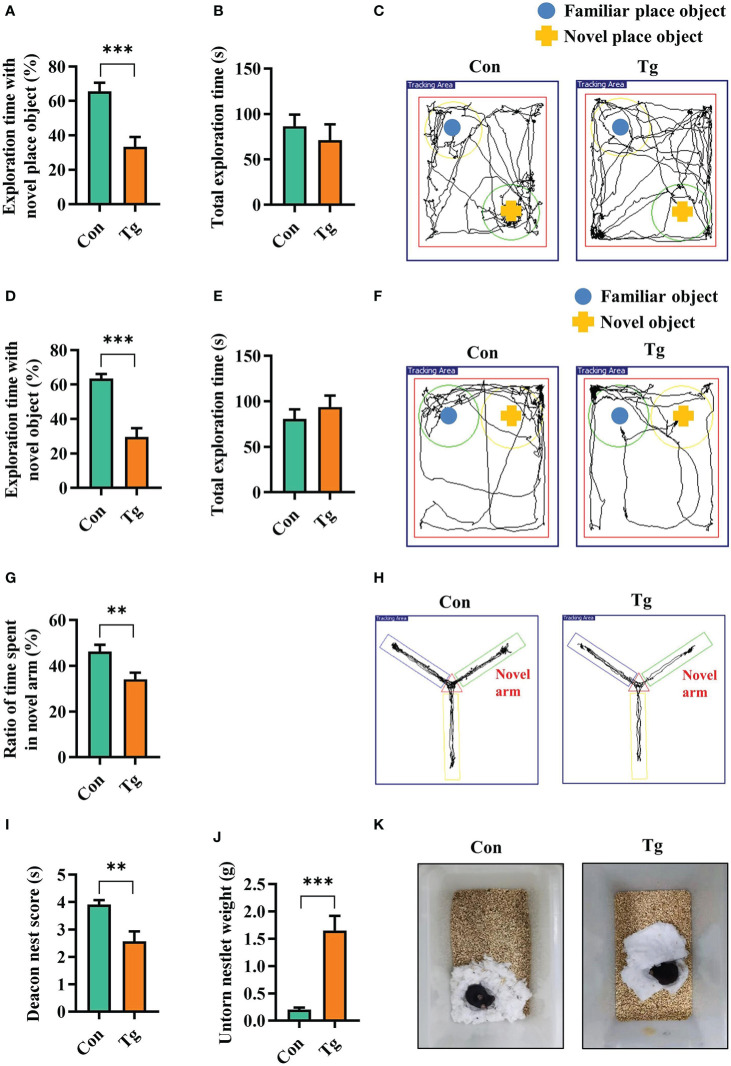
Figure 1.
T. gondii chronic infection impairs cognitive function in mice. (A) Percentage of time spent with the object in the novel place to total object exploration time and (B) the total object exploration time in the novel location test were recorded. (C) Representative track plots of Con and Tg groups recorded by SMART video tracking system in the testing phase. (D) Percentage of time spent with the novel object to total object exploration time and (E) the total object exploration time in the novel object recognition test were recorded. (F) Representative track plots of Con and Tg groups recorded by SMART video tracking system. (G) Percentage of time spent with the novel arm to total arm exploration time in Y-maze spatial memory test. (H) Representative example of spatial memory in the Y-maze test recorded by SMART video tracking system. Note that the control mouse spent more time exploring the novel arm whereas the mice infected with T. gondii did not show preference to the novel arm. (I) The nest score and (J) untorn nestlet weight (amount of untorn nesting material) (n = 10 mice for each group). (K) Representative images of nesting result in Con and Tg groups. Con, control mice; Tg, T. gondii infected mice. Values are mean ± SEM. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.