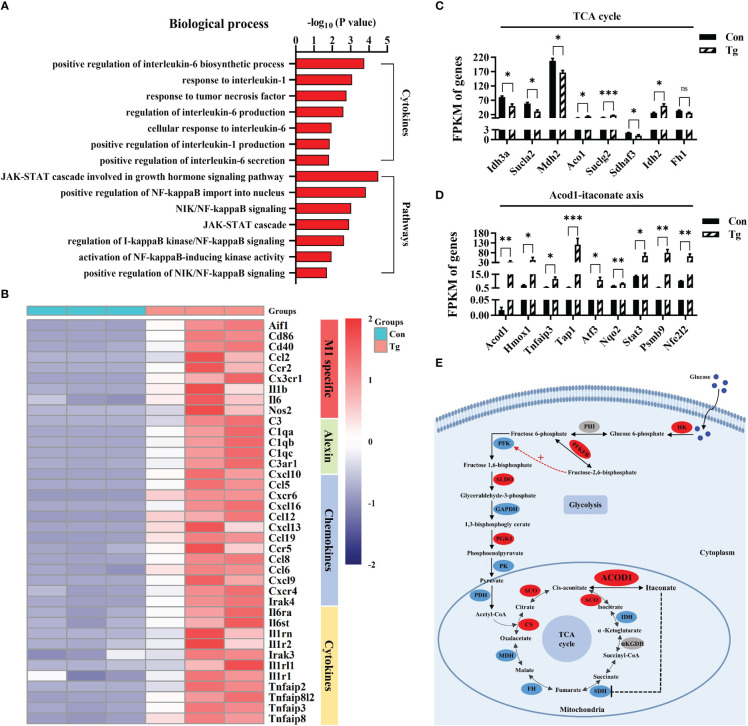
Figure 3.
T. gondii chronic infection triggers extensive neuroinflammation along with disorder of the Acod1/itaconate axis in the hippocampus of mice. (A) The biological processes associated with cytokines and inflammatory pathways are upregulated in T. gondii infected mice. (B) Heatmap demonstrating the relative expression of core genes related to M1 specific, alexin, chemokines and cytokines in the enrichment plot (n = 3) are upregulated in Tg group in comparison to Con group. Normalized expression of selected genes regulating (C) TCA cycle and (D) Acod1-itaconate axis. (E) The overview of metabolic reprogramming in hippocampus in T. gondii infected mice. The metabolism diagram shows the expression profile of key enzymes. Glycolysis pathways were significantly upregulated while TCA cycle were dramatically broken. Enzymes identified in our study are marked in red oval (upregulated) and blue oval (downregulated), while other enzymes are marked in grey oval. Hk, hexokinase; Phi, phosphate isomerase; Pfkfb, fructose-2,6-biphosphatase; Pfk, phosphofructokinase; Aldo, aldolase; Gapdh, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Pgk1, phosphoglycerate kinase 1; Pk, pyruvate kinase; Pdh, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; Cs, citrate synthase; Aco, aconitase; Acod1, aconitate decarboxylase 1; Idh, isocitrate dehydrogenase; αKGDH, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase; Sdh, succinate dehydrogenase; Fh, fumarate hydratase; Mdh, malate dehydrogenase. Con, control mice; Tg, T. gondii infected mice. Values are mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.