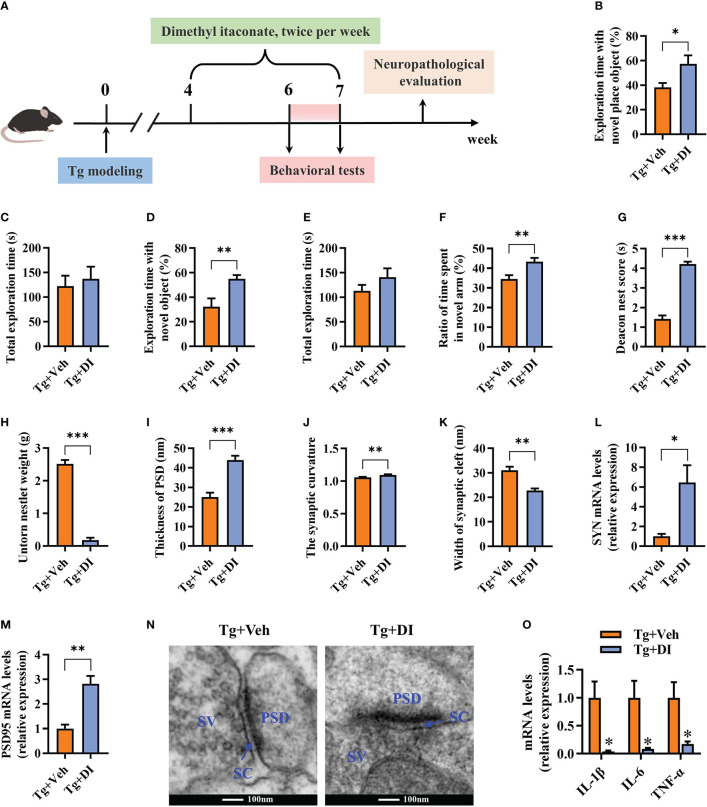
Figure 7.
Dimethyl itaconate has the therapeutic effect on T. gondii-induced cognitive and synaptic impairments in mice. (A) Schematic timeline for DI therapeutic effect on cognitive deficits induced by T. gondii infection in mice. (B) Percentage of time spent with the object in the novel place to total object exploration time and (C) the total object exploration time in the novel location test were recorded. (D) Percentage of time spent with the novel object to total object exploration time and (E) the total object exploration time in the novel object recognition test were recorded. (F) Percentage of time spent with the novel arm to total arm exploration time in Y-maze spatial memory test. (G) The nest score and (H) untorn nestlet weight (amount of untorn nesting material) (n = 10 mice for each group). (I–K) Image analysis of the thickness of postsynaptic density (PSD), the synaptic curvature, and width of the synaptic cleft (SC) (n = 2, 10 images per mouse). (L, M) The mRNA expression of SYN and PSD95 in the hippocampus (n = 3). (N) The ultrastructure of synapses in the hippocampus CA1 region of mice in Tg+Veh group compared with Tg+DI group on the electron micrograph (scale bar 100 nm). (O) The mRNA expression of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in the hippocampus (n = 3). Tg+Veh, T. gondii infected mice with vehicle control treatment; Tg+DI: T. gondii infected mice with DI treatment. Values are mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.