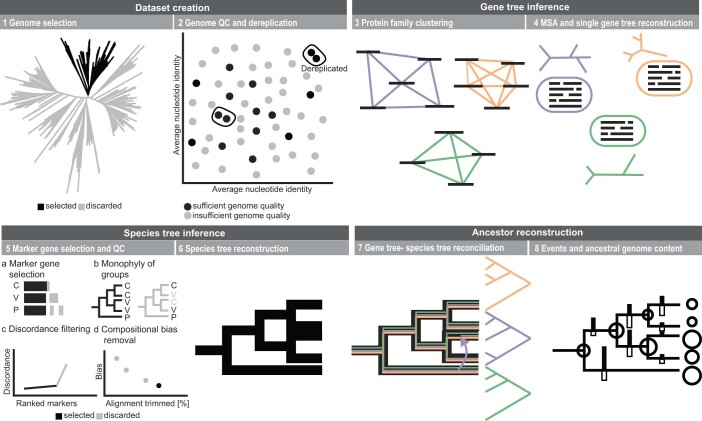
Extended Data Fig. 1. Workflow for ancestral state reconstruction of Chlamydiae.
Dataset creation: PVC bacteria representatives from public repositories were selected with completeness ≥90% and redundancy ≤2%. Species and genus-level representatives were selected for Chlamydiae and non-Chlamydiae PVC members, respectively. Gene tree inference: Protein sequences from the selected dataset were clustered into NOG gene families at the last universal common ancestor level. Unmapped protein sequences were de novo clustered. Protein sequences from each resulting gene family were aligned into a multiple sequence alignment (MSA) and ML single-gene trees inferred. Species tree inference: Gene families found in a single-copy in at least 95% of dataset taxa were selected as potential marker genes. ML single-gene trees were inferred and manually curated, with marker genes that well-resolved PVC phyla retained; further marker genes were removed through discordance filtering, while distant homologs, paralogs, and redundant sequences were removed for each retained marker gene. Individually aligned protein sequences from each marker gene were then concatenated into a supermatrix alignment that was used for both ML and Bayesian phylogenetic inference, with compositionally heterogeneous sites sequentially removed to reduce bias. Ancestor reconstruction: ancestral states were reconstructed using gene-tree species-tree reconciliation. See Methods for details.