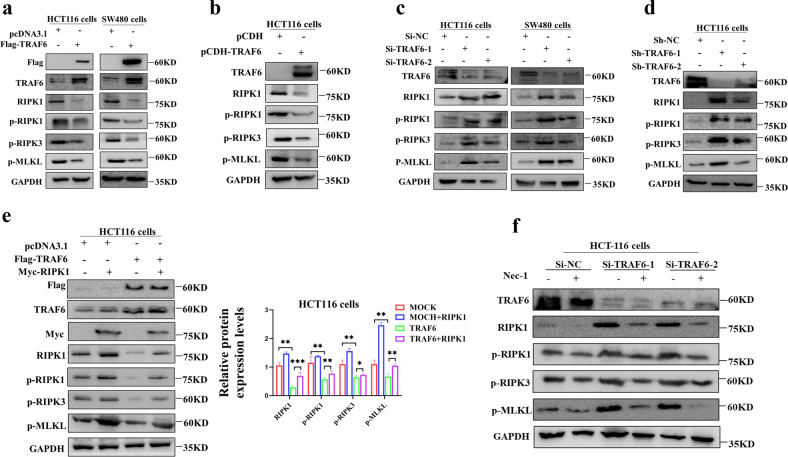
Fig. 4. TRAF6 regulates the RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL signaling axis.
a An HCT116 and SW480 cells were transiently transfected with Flag-TRAF6 or mock control plasmid. Protein levels of RIPK1, p-RIPK1, p-RIPK3, and p-MLKL were detected in western blotting. b HCT116 cells were stably transfected with Flag-TRAF6 or mock control plasmid. Protein levels of RIPK1, p-RIPK1, p-RIPK3, and p-MLKL were detected by western blottng. c HCT116 and SW480 cells were transiently transfected with Si-NC, Si-TRAF6-1, or Si-TRAF6-1 plasmids. Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of RIPK1, p-RIPK1, p-RIPK3, and p-MLKL. d HCT116 cells were stably transfected with Sh-NC, Sh-TRAF6-1, or Sh-TRAF6-1 plasmids. Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of RIPK1, p-RIPK1, p-RIPK3, and p-MLKL. e HCT16 cells were co-transfected with Flag-TRAF6 and Myc-RIPK1 plasmids, Protein levels of RIPK1, p-RIPK1, p-RIPK3, and p-MLKL were detected in western blotting. f HCT116 cells were transiently transfected with Si-NC, Si-TRAF6-1, or Si-TRAF6-2 plasmids and incubated with Nec-1. Western blotting was used to detect RIPK1, p-RIPK1, p-RIPK3, and p-MLKL protein levels. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, with one-way ANOVA analysis (e)).