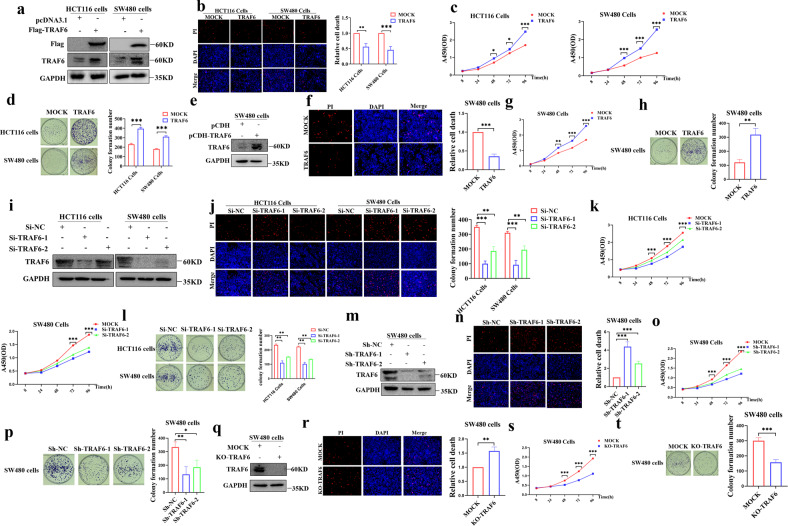
Fig. 5. TRAF6 inhibits necroptosis to promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation.
a–d HCT116 and SW480 cells were transiently transfected with Flag-TRAF6 or mock control plasmid. Western blotting was used to detect the levels of TRAF6 protein (a). The transfected cells were further examined and analyzed for necroptosis (b), as well as cell proliferation (c) and clonal colony formation assays (d). e–h SW480 cells were stably transfected with Flag-TRAF6 or mock control plasmid. Western blotting was used to detect the levels of TRAF6 protein (e). The transfected cells were analyzed for necroptosis (f), as well as cell proliferation (g) and clonal colony formation experiments (h). i–l HCT116 and SW480 cells were transiently transfected with Si-NC, Si-TRAF6-1, or Si-TRAF6-1 plasmids. Western blotting was used to detect the levels of TRAF6 protein (i). The transfected cells were further tested and analyzed for necroptosis (j), as well as cell proliferation (k) and clonal colony formation experiments (l). m–p SW480 cells were stably transfected with Sh-NC, Sh-TRAF6-1, or Sh-TRAF6-1 plasmids. Western blotting was used to detect levels of TRAF6 protein (m). The transfected cells were further tested and analyzed for necroptosis (n), as well as cell proliferation (o) and clonal colony formation experiments (p). q–t SW480 cells were transiently transfected with KO-TRAF6 or mock control plasmid. Western blotting was used to detect the levels of TRAF6 protein (q). The transfected cells were analyzed for necroptosis (r), as well as cell proliferation (s) and clonal colony formation experiments (t). (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, with an unpaired Student’s t test (b–d, f–h, r–t) or one-way ANOVA analysis (j–l, n–p)).