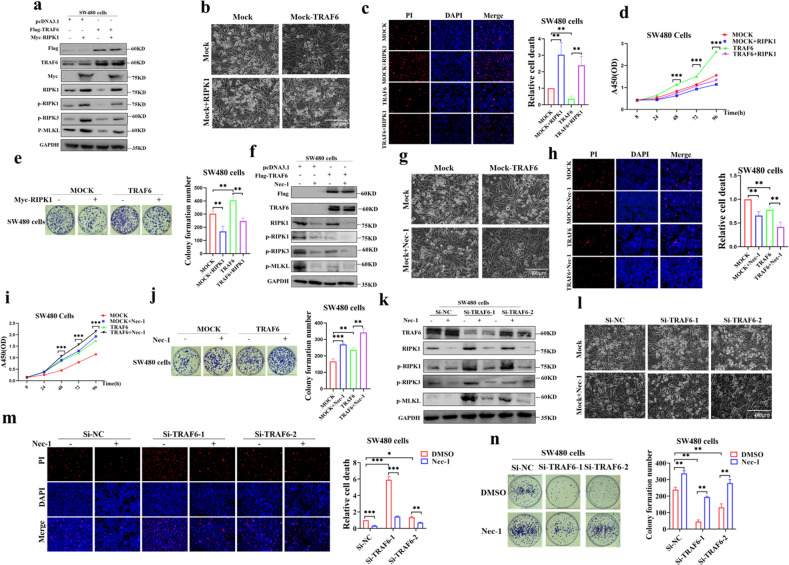
Fig. 6. TRAF6 promotes cell proliferation by inhibiting colorectal necroptosis through the RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL axis.
a–e SW480 cells were co-transfected with Flag-TRAF6 and Myc-RIPK1 plasmids. Protein levels of TRAF6, RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL were detected in western blotting (a). The images were obtained by light microscopy (b). Necroptosis of the transfected cells was detected and analyzed (c), as well as cell proliferation (d) and clonal colony formation (e). f–j SW480 cells were transfected with Flag-TRAF6 or mock plasmid and incubated with Nec-1. The protein levels of TRAF6, RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL were detected in western blotting (f). The images were obtained in light microscopy (g). Necroptosis of the transfected cells was analyzed (h), as well as cell proliferation (i) and clonal colony formation (j). k–n SW480 cells were transiently transfected with Si-NC, Si-TRAF6-1, or Si-TRAF6-1 plasmids and incubated with Nec-1. The protein levels of TRAF6, RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL were detected in western blotting (k). Images were obtained in light microscopy (l). Necroptosis of the transfected cells was analyzed (m) and clonal colony formation (n). (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, with one-way ANOVA analysis (c–e, h–j, m, n)).