FIGURE 5.
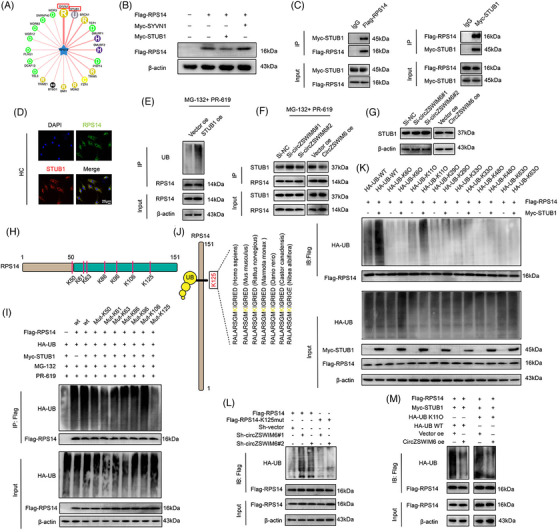
STUB1 is an E3 ligase of ribosomal protein S14 (RPS14), and K125 is the primary ubiquitylation site of RPS14: (A) prediction of potential E3 ligase of RPS14; (B) western blot analysis of FLAG–RPS14 protein level after Myc‐STUB1 and Myc‐SYVN1 transfection, respectively; (C) HEK‐293T cells are transfected with FLAG–RPS14 or Myc‐STUB1. Consecutive immunoprecipitation (Co‐IP) shows interaction between FLAG–RPS14 and Myc‐STUB1. IgG as the negative control; (D) co‐localization of RPS14 (green) and STUB1 (red) in human chondrocyte indicated by immunofluorescence; (E) the ubiquitination level of RPS14 after STUB1 overexpression; (F) effect of CircZSWIM6 knock‐down or overexpression on the interaction between STUB1 and RPS14 in human chondrocyte; (G) western blot analysis of STUB1 protein level after CircZSWIM6 knock‐down or overexpression in human chondrocyte; (H) illustration of ubiquitylation site on RPS14; (I) human chondrocyte transfected with FLAG‐tagged wild‐type or mutant RPS14 KR plasmid and subsequently performed with immunoprecipitation (IP). RPS14 ubiquitylation is tested by western blot analysis; (J) conservation ability of the K125 site of RPS14 among different species; (K) human chondrocyte expressing FLAG–RPS14 and different ubiquitylation types with or without Myc‐STUB1. Ubiquitylation types of RPS14 induced by STUB1 are verified by western blot analysis; (L) effect of CircZSWIM6 knock‐down on the K125R RPS14 ubiquitylation in human chondrocyte; (M) effect of CircZSWIM6 overexpression on K11 ubiquitylation level of RPS14 in human chondrocyte; quantitative data shown as mean ± SD; exact p‐values are shown in figures. Two‐side unpaired Student's t‐test was used for statistical analysis. One‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison was used for statistical analysis.
