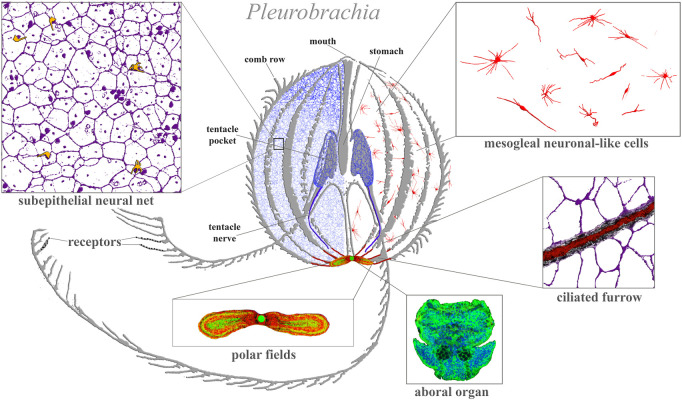
FIGURE 1.
Ctenophore neural systems. As an illustrated example, the schematic diagram is based on the recent study of the cydippid Pleurobrachia bachei (Norekian and Moroz, 2016; 2019b). Different colors indicate different cellular populations. Most neurons and receptors (yellow) are located within the subepithelial neural net in the skin (blue, magenta) and tentacle shields with two tentacular nerves (dark blue). There are two concentrations of neural elements: one in the aboral organ (green) with densely packed neurons and other cell types (the elementary brain?); and the second in the polar fields putative chemosensory structures (yellow/green, red marks phalloidin-labeled elements). The mesoglea has a diffuse population of neuron-like cells (red). Eight ciliated furrows (conductive ciliated cells—red lines) connect the aboral organ with comb plates. The ciliated furrows are closely associated with neural net elements (insert) and are possible under neuronal control.