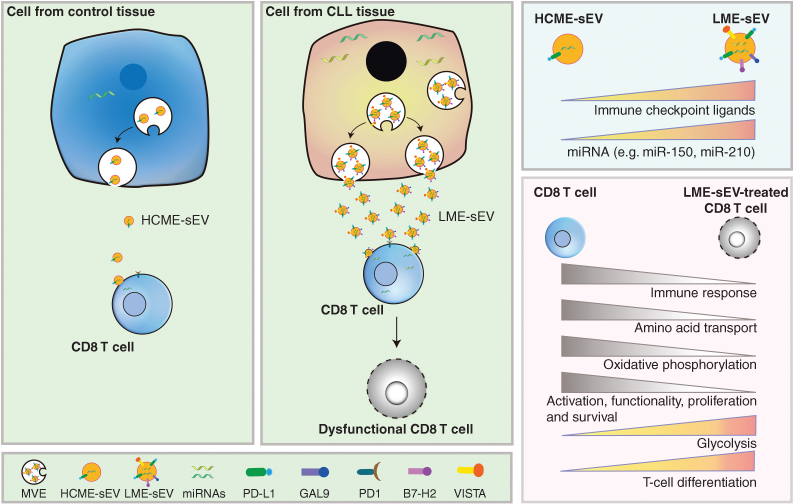
Figure 1.
Cells from CLL tissues secrete a higher level of sEVs (LME-sEVs) compared with cells from control tissue (HCME-sEVs). With immune-checkpoint ligands (e.g., PD-L1, GAL9, and VISTA) and miRNAs (e.g., miR-150, miR-210), LME-sEVs suppress CD8 T-cell function by changing their transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome. HCME-sEV, healthy control tissue-derived small extracellular vesicle; GAL9, galectin-9; PD-1, programmed death-1; B7-H2, programmed death-ligand 2; VISTA, V-domain Ig suppressor of T-cell activation.