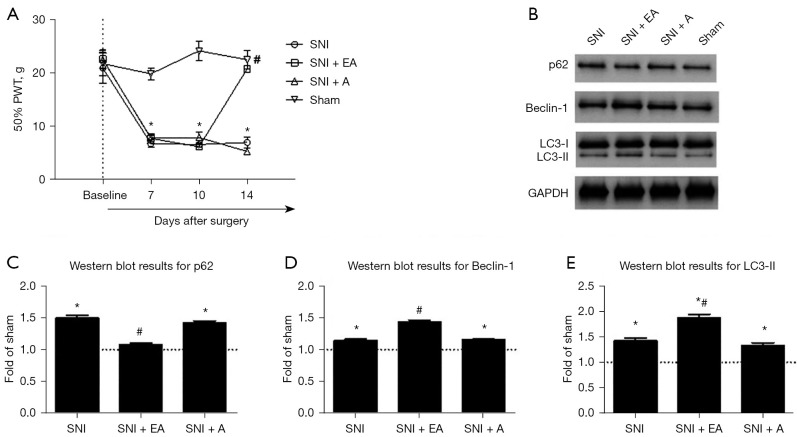
Figure 1.
Effects of repetitive EA on mechanical hypersensitivity and the expression of autophagy-related proteins (p62, Beclin-1, and LC3-II) in rats after SNI. (A) SNI (n=6) induced severe mechanical allodynia from day 7 after surgery, which persisted until day 14. The PWT in sham-operated rats (n=6) did not change significantly from baseline during the testing period. From day 7 to day 14 after surgery, EA (n=6) significantly increased the PWT. In the control group for EA, acupuncture (n=6), did not significantly increase the PWT in SNI rats. (B) Illustrative immunoblots showing p62, Beclin-1, and LC3-II expression in the ipsilateral lumbar spinal cord of SNI rats (n=3), SNI rats administered EA (n=3) or acupuncture (n=3), and sham-operated rats (n=3). (C-E) Quantification of the protein levels for p62, Beclin-1, and LC3-II from the ipsilateral lumbar spinal cord among the distinct groups. All of the data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean. *, P<0.05 versus the sham group; #, P<0.05 versus the SNI group, two-way mixed-model ANOVA. SNI, spared nerve injury; A, acupuncture; EA, electroacupuncture; PWT, paw withdrawal threshold; ANOVA, analysis of variance.