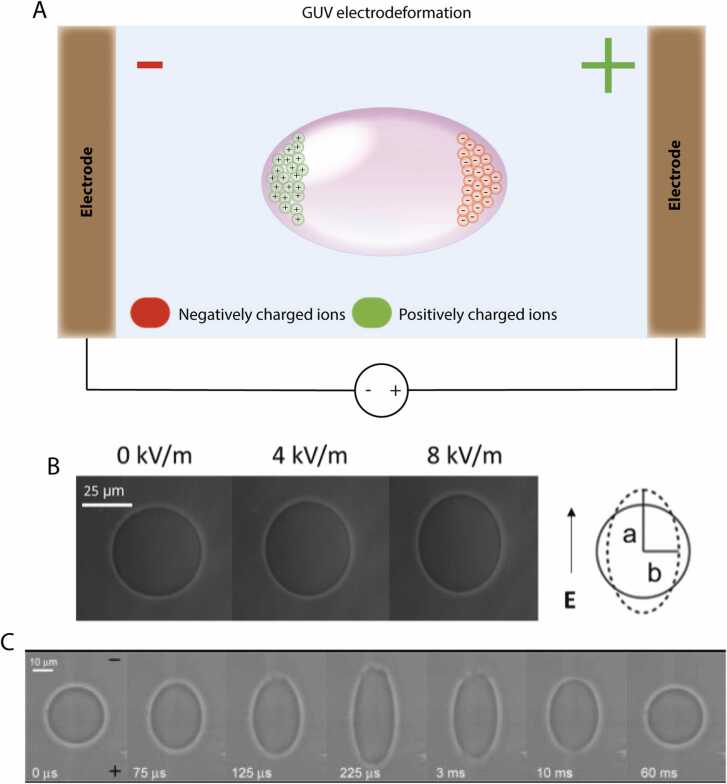
Fig. 5.
Electrodeformation of GUVs. (A) Schematic representation of an electrodeformed GUV. Two parallel electrodes connected to a voltage source induce an electric field across a conductive GUV-containing solution. Charged ions inside GUV separate towards the opposing sides of the electrodes. This charge separation results in the deformation of GUVs. (B) Elliptical deformation of a GUV in response to an AC electric field. Deformation profiles of GUVs are used to measure membrane bending rigidity and membrane capacitance. (C) Electrodeformation of GUVs using DC pulses. Dynamic response of GUVs to electric field, including elliptical deformation and poration are captured at high temporal resolution. These dynamic responses are used to measure the critical transmembrane potential of GUV lipid bilayer. Panels B and C are adapted from [142] and [144], respectively