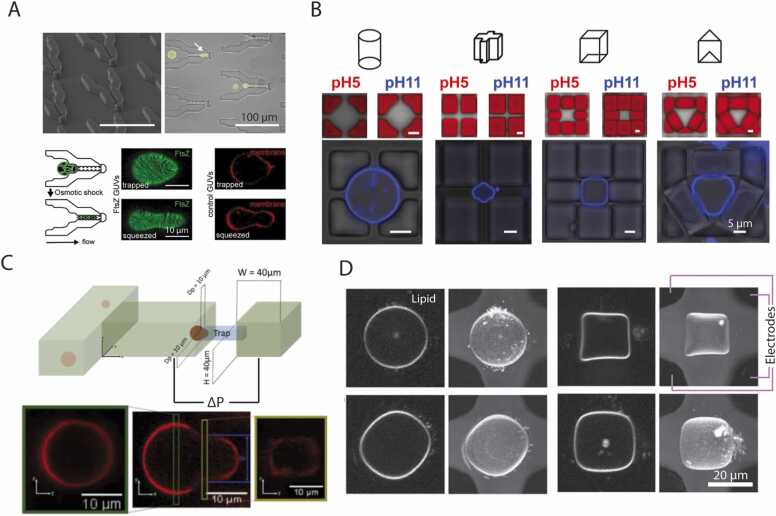
Fig. 6.
Microfluidic manipulation of GUVs. (A) FtsZ-encapsulating GUVs trapped and deformed using a microfluidic device (top). Modulating the osmotic condition of the GUV solution changes GUV deformation and FtsZ organization (bottom). (B) A chemically tunable microfluidic device is used to trap and shape GUVs. Different trapping designs are used to tarp GUVs. Increasing solution pH results in swelling of trapping features, thus deforming the GUVs to specific shapes. (C) Implementation of micropipette aspiration in a microfluidic device. GUVs are trapped and aspirated in to a microchannel. Changing the flow rate inside the microfluidic channel results in change in aspiration pressure ΔP. (D) Integrated microfluidic device with electric field cages trap deform and reorient GUVs. Panels A, B, C, and D are adapted from [22], [163], [164], and [165], respectively.